The effective use of parallel cores in a Java program has always been challenging. Few home-grown frameworks would distribute the work across multiple cores and then join them to return the result set. Java 7 incorporated this feature as a Fork and Join framework.
1. Fork/Join Framework
The Fork-Join breaks the task at hand into sub-tasks until the mini-task is simple enough to solve it without further breakups. It’s like a divide-and-conquer algorithm. One crucial concept in this framework is that no worker thread is idle. They implement a work-stealing algorithm in that idle workers steal the work from those workers who are busy.
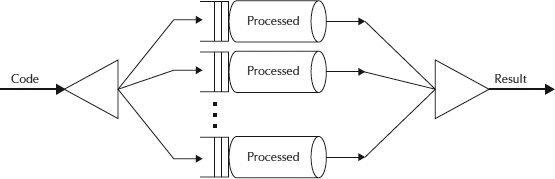
It’s based on the work of Doug Lea, a thought leader on Java concurrency. Fork/Join deals with the threading hassles; you indicate to the framework which portions of the work can be broken apart and handled recursively.
Result solve(Problem problem) {
if (problem is small)
directly solve problem
else {
split problem into independent parts
fork new subtasks to solve each part
join all subtasks
compose result from subresults
}
}2. Core Classes
The core classes supporting the Fork-Join mechanism are ForkJoinPool and ForkJoinTask.
Let’s learn about their roles in detail.
2.1. ForkJoinPool
The ForkJoinPool is a specialized implementation of ExecutorService implementing the work-stealing algorithm discussed above. We create an instance of ForkJoinPool by providing the target parallelism level i.e., the number of processors.
If you use a no-argument constructor, by default, it creates a pool of size that equals the number of available processors obtained using the given technique.
var numberOfProcessors = Runtime.getRunTime().availableProcessors();
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(numberOfProcessors);Although you specify any initial pool size, the pool adjusts its size dynamically to maintain enough active threads at any given time. Another significant difference compared to other ExecutorService's is that this pool need not be explicitly shutdown upon program exit because all its threads are in daemon mode.
There are three different ways of submitting a task to the ForkJoinPool.
- execute() – Desired asynchronous execution; call its fork method to split the work between multiple threads.
- invoke() – Await to obtain the result; call the invoke method on the pool.
- submit() – Returns a Future object that you can use for checking the status and getting the result on its completion.
2.2. ForkJoinTask
ForkJoinTask is an abstract class for creating tasks that run within a ForkJoinPool. The Recursiveaction and RecursiveTask are the only two direct, known subclasses of ForkJoinTask.
The only difference between these two classes is that the RecursiveAction does not return a value while RecursiveTask does have a return value and returns an object of the specified type.
In both cases, you would need to implement the compute() method in your subclass that performs the main computation desired by the task.
The ForkJoinTask class provides several methods for checking the execution status of a task.
- isDone(): returns true if a task completes in any way.
- isCompletedNormally(): returns true if a task completes without cancellation or encountering an exception.
- isCancelled(): returns true if the task was cancelled.
- isCompletedabnormally(): returns true if the task was either cancelled or threw an exception.
3. Fork/Join Pool Example
In this example, we will learn how to use the asynchronous methods provided by the ForkJoinPool and ForkJoinTask classes for the management of tasks.
3.1. Example
We will implement a program that will search for files with a specified extension inside a folder and its subfolders. The ForkJoinTask class we will implement will process the content of a folder.
Each subfolder inside that folder will send a new task to the ForkJoinPool class asynchronously. For each file inside that folder, the task will check the file’s extension and add it to the result list if it proceeds.
The solution to the above problem is implemented in FolderProcessor class, which is given below:
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
public class FolderProcessor extends RecursiveTask<List<String>> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//This attribute will store the full path of the folder this task is going to process.
private final String path;
//This attribute will store the name of the extension of the files this
// task is going to look for.
private final String extension;
//Implement the constructor of the class to initialize its attributes
public FolderProcessor(String path, String extension) {
this.path = path;
this.extension = extension;
}
//Implement the compute() method. As you parameterized the RecursiveTask class with the List<String> type,
//this method has to return an object of that type.
@Override
protected List<String> compute() {
//List to store the names of the files stored in the folder.
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
//FolderProcessor tasks to store the subtasks that are going to process the subfolders stored in the folder
List<FolderProcessor> tasks = new ArrayList<FolderProcessor>();
//Get the content of the folder.
File file = new File(path);
File content[] = file.listFiles();
//For each element in the folder, if there is a subfolder, create a new FolderProcessor object
//and execute it asynchronously using the fork() method.
if (content != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < content.length; i++) {
if (content[i].isDirectory()) {
FolderProcessor task = new FolderProcessor(content[i].getAbsolutePath(), extension);
task.fork();
tasks.add(task);
}
//Otherwise, compare the extension of the file with the extension you are looking for using the checkFile() method
//and, if they are equal, store the full path of the file in the list of strings declared earlier.
else {
if (checkFile(content[i].getName())) {
list.add(content[i].getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
}
//If the list of the FolderProcessor subtasks has more than 50 elements,
//write a message to the console to indicate this circumstance.
if (tasks.size() > 50) {
System.out.printf("%s: %d tasks ran.\n", file.getAbsolutePath(),
tasks.size());
}
//add to the list of files the results returned by the subtasks launched by this task.
addResultsFromTasks(list, tasks);
return list;
}
//For each task stored in the list of tasks, call the join() method that
// will wait for its finalization and then will return the result of the task.
//Add that result to the list of strings using the addAll() method.
private void addResultsFromTasks(List<String> list, List<FolderProcessor> tasks) {
for (FolderProcessor item : tasks) {
list.addAll(item.join());
}
}
//This method compares if the name of a file passed as a parameter ends with the extension you are looking for.
private boolean checkFile(String name) {
return name.endsWith(extension);
}
}And to use above FolderProcessor, follow the below code:
public class ForkJoinExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
FolderProcessor system = new FolderProcessor("C:\\Windows", "log");
FolderProcessor apps = new FolderProcessor("C:\\Program Files", "log");
FolderProcessor documents = new FolderProcessor("C:\\Documents And Settings", "log");
//Execute the three tasks in the pool using the execute() method.
pool.execute(system);
pool.execute(apps);
pool.execute(documents);
//Write to the console information about the status of the pool every second
//until the three tasks have finished their execution.
do {
System.out.printf("******************************************\n");
System.out.printf("Main: Parallelism: %d\n", pool.getParallelism());
System.out.printf("Main: Active Threads: %d\n",
pool.getActiveThreadCount());
System.out.printf("Main: Task Count: %d\n", pool.getQueuedTaskCount());
System.out.printf("Main: Steal Count: %d\n", pool.getStealCount());
System.out.printf("******************************************\n");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} while ((!system.isDone()) || (!apps.isDone()) || (!documents.isDone()));
pool.shutdown();
//Write the number of results generated by each task to the console.
List<String> results;
results = system.join();
System.out.printf("System: %d files found.\n", results.size());
results = apps.join();
System.out.printf("Apps: %d files found.\n", results.size());
results = documents.join();
System.out.printf("Documents: %d files found.\n", results.size());
}
}The output of the above program will look like this:
Main: Parallelism: 2
Main: Active Threads: 3
Main: Task Count: 1403
Main: Steal Count: 5551
******************************************
******************************************
Main: Parallelism: 2
Main: Active Threads: 3
Main: Task Count: 586
Main: Steal Count: 5551
******************************************
System: 337 files found.
Apps: 10 files found.
Documents: 0 files found.3.2. Analysis
In the FolderProcessor class, Each task processes the content of a folder. As you know, this content has the following two kinds of elements:
- Files
- Other folders
If the task finds a folder, it creates another Task object to process that folder and sends it to the pool using the fork() method. This method sends the task to the pool that will execute it if it has a free worker thread, or it can create a new one.
The method returns immediately, so the task can continue processing the folder’s content. For every file, a task compares its extension with the one it’s looking for and, if they are equal, adds the file’s name to the list of results.
Once the task has processed the assigned folder’s content, it waits for the finalization of all the tasks it sent to the pool using the join() method.
This method, called in a task, waits for the finalization of its execution and returns the value returned by the compute() method. The task groups the results of all the tasks it sent with its results and returns that list as a return value of the compute() method.
4. Difference between ForkJoinPool And ExecutorService
The work-stealing algorithm is the main difference between the Fork/Join and the Executor framework.
Unlike the Executor framework, when a task is waiting for the finalization of the sub-tasks it has created using the join operation, the thread executing that task (called worker thread ) looks for other tasks that have not been executed yet and begins its execution.
In this way, the threads take full advantage of their running time, thereby improving the application’s performance.
5. Existing Fork/Join Implementations in JDK
Some very helpful features in Java SE have already been implemented using the fork/join framework.
- One such implementation, introduced in Java SE 8, is used by the java.util.Arrays class for its parallelSort() methods. These methods are similar to sort(), but leverage concurrency via the fork/join framework. Parallel sorting of large arrays is faster than sequential sorting on multiprocessor systems.
- Parallelism used in Stream.parallel(). Read more about this parallel stream operation in java 8.
6. Conclusion
Designing good multi-threaded algorithms is hard, and fork/join doesn’t work in every circumstance. It is beneficial within its own domain of applicability. Still, in the end, you have to decide whether your problem fits within the framework, and if not, you must be prepared to develop your own solution, building on the superb tools provided by java.util.concurrent package.
Happy Learning !!

Comments