Learn to create and manage many-to-many relationships between entities in a hibernate/JPA-based applications using @ManyToMany annotation.
A many-to-many association is made between two entities where one entity can be associated with multiple other instances of the other entity. For example, for a subscription service, SubscriptionEntity and ReaderEntity can be two types of entities. A given subscription can have multiple readers, whereas a reader can subscribe to multiple subscriptions.
1. Design Overview
The @ManyToMany association requires a link table that joins two entities. Note that @ManyToMany can be either unidirectional or bidirectional.
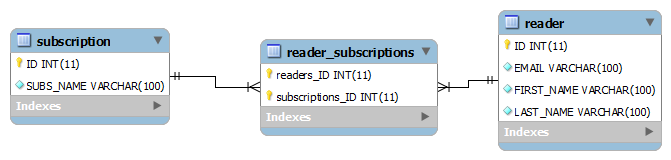
To demonstrate many to many mapping using hibernate annotations, we will associate two entities i.e. ReaderEntity and SubscriptionEntity. Their database schema is given in the image. Using these tables, any application can save multiple associations between readers and subscriptions.
1.1. Unidirectional
This is the preferred approach in most cases. We should apply @ManyToMany annotation only on the owning side of the relationship.
public class SubscriptionEntity {
@Id
@Column(name = "ID")
private Integer subscriptionId;
@Column
private String subscriptionName;
@ManyToMany(cascade = {CascadeType.PERSIST, CascadeType.MERGE})
private Set<ReaderEntity> readers;
}
public class ReaderEntity {
@Id
@Column(name = "ID")
private Integer readerId;
@Column
private String email;
}1.2 Bidirectional
A bidirectional @ManyToMany association has an owning and a mappedBy side.
public class SubscriptionEntity {
@Id
@Column(name = "ID")
private Integer subscriptionId;
@Column
private String subscriptionName;
@ManyToMany(cascade = {CascadeType.PERSIST, CascadeType.MERGE})
private Set<ReaderEntity> readers;
}
public class ReaderEntity {
@Id
@Column(name = "ID")
private Integer readerId;
@Column
private String email;
@ManyToMany(mappedBy = "readers")
private Set<ReaderEntity> subscriptions;
}2. Owning Side Entity
The relationship owning entity is the entity that is responsible make making the association and maintaining it. In our case, I am making ReaderEntity the owner entity. @JoinTable annotation has been used to make this association.
The link table is controlled by the owning side. When an entity is removed from the @ManyToMany collection, Hibernate simply deletes the joining record in the link table.
Avoid using CascadeType.REMOVE because it will propagate beyond the link table. Since the mapped entities (to-be-deleted) might be referenced by other entities on the parent-side, the automatic removal might end up in a ConstraintViolationException.
So, the good practice is just to remove the parent record and Hibernate will remove the associated link records.
@Entity(name = "ReaderEntity")
@Table(name = "READER", uniqueConstraints = {
@UniqueConstraint(columnNames = "ID"),
@UniqueConstraint(columnNames = "EMAIL")})
public class ReaderEntity implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "ID", unique = true, nullable = false)
private Integer readerId;
@ManyToMany(cascade = {CascadeType.PERSIST, CascadeType.MERGE})
@JoinTable(name = "READER_SUBSCRIPTIONS", joinColumns =
{@JoinColumn(referencedColumnName = "ID")}
, inverseJoinColumns = {@JoinColumn(referencedColumnName = "ID")})
private Set<SubscriptionEntity> subscriptions;
//Other fields, getters, setters are hidden for brevity
}3. Mapped Entity
Our mapped entity is SubscriptionEntity which is mapped to ReaderEntity using “mappedBy” attribute. It is done in the bi-directional association.
@Entity(
@Table(name = "SUBSCRIPTION", uniqueConstraints = {
@UniqueConstraint(columnNames = "ID")})
public class SubscriptionEntity implements Serializable
{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "ID", unique = true, nullable = false)
private Integer subscriptionId;
@Column(name = "SUBS_NAME", unique = true, nullable = false, length = 100)
private String subscriptionName;
@ManyToMany(mappedBy = "subscriptions")
private Set<ReaderEntity> readers;
//Other fields, getters, setters are hidden for brevity
}4. Demo
Now, it’s time to test the code. I have written the following code to test the above entities and their many-to-many relationship.
// Add subscription
SubscriptionEntity subOne = new SubscriptionEntity();
subOne.setSubscriptionName("Entertainment");
SubscriptionEntity subTwo = new SubscriptionEntity();
subTwo.setSubscriptionName("Horror");
Set<SubscriptionEntity> subs = new HashSet<SubscriptionEntity>();
subs.add(subOne);
subs.add(subTwo);
// Add readers
ReaderEntity readerOne = new ReaderEntity();
readerOne.setEmail("demo-user1@mail.com");
readerOne.setFirstName("demo");
readerOne.setLastName("user");
ReaderEntity readerTwo = new ReaderEntity();
readerTwo.setEmail("demo-user2@mail.com");
readerTwo.setFirstName("demo");
readerTwo.setLastName("user");
Set<ReaderEntity> readers = new HashSet<ReaderEntity>();
readers.add(readerOne);
readers.add(readerTwo);
readerOne.setSubscriptions(subs);
readerTwo.setSubscriptions(subs);
session.save(readerOne);
session.save(readerTwo);Program Output:
Hibernate: insert into READER (EMAIL, FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME) values (?, ?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into SUBSCRIPTION (SUBS_NAME) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into SUBSCRIPTION (SUBS_NAME) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into READER (EMAIL, FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME) values (?, ?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into READER_SUBSCRIPTIONS (readers_ID, subscriptions_ID) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into READER_SUBSCRIPTIONS (readers_ID, subscriptions_ID) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into READER_SUBSCRIPTIONS (readers_ID, subscriptions_ID) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into READER_SUBSCRIPTIONS (readers_ID, subscriptions_ID) values (?, ?)In this example, we learned about hibernate many to many join table using annotations.
Happy Learning !!

Comments