In JMS tutorial, you read about JMS messaging domains Point to Point Domain and Publish Subscribe Domain. In this example, we will go through one such example of point to point messaging domain. In point to point message the sender delivers the message to the queue and a single receiver takes out the message from the queue. The receiver does not need to be listening to the queue at the time the message is sent.
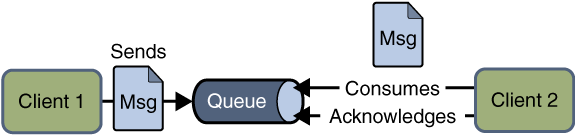
Point-To-Point Messaging Publisher Application Flow
A typical point-to-point messaging example for the sender application is given below. The following steps for the application are –
- Firstly, we will obtain the Initial Context object for the JMS server.
- After that use the initial context object for lookup a queue object.
- Again we will use the initial context object for lookup the queue connection factory.
- Then use the queue connection factory to create the queue connection as it represents the physical connection of the JMS server.
- After creating the queue connection factory we will create the queue session where the first parameter will decide whether the session is transacted or not. But we will use a non-transacted session.
- After this create a queue sender for queue and then create a message.
- Then send the message such as “Hello World” to the queue object.
- After that close the queue connection as you close the queue connection it will automatically close the session and queue sender.
Let’s look at example below:
package pointToPoint;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.jms.Queue;
import javax.jms.Session;
import javax.jms.TextMessage;
import javax.jms.QueueSender;
import javax.jms.DeliveryMode;
import javax.jms.QueueSession;
import javax.jms.QueueConnection;
import javax.jms.QueueConnectionFactory;
public class Sender
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// get the initial context
InitialContext context = new InitialContext();
// lookup the queue object
Queue queue = (Queue) context.lookup("queue/queue0");
// lookup the queue connection factory
QueueConnectionFactory conFactory = (QueueConnectionFactory) context.lookup ("queue/connectionFactory");
// create a queue connection
QueueConnection queConn = conFactory.createQueueConnection();
// create a queue session
QueueSession queSession = queConn.createQueueSession(false, Session.DUPS_OK_ACKNOWLEDGE);
// create a queue sender
QueueSender queSender = queSession.createSender(queue);
queueSender.setDeliveryMode(DeliveryMode.NON_PERSISTENT);
// create a simple message to say "Hello World"
TextMessage message = queSession.createTextMessage("Hello World");
// send the message
queSender.send(message);
// print what we did
System.out.println("Message Sent: " + message.getText());
// close the queue connection
queConn.close();
}
}
Point-To-Point Messaging Subscriber Application Flow
Most of the steps for the receiver side are same as for the sender application – except it will listen the message rather than sending the JMS message.
package pointToPoint;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.jms.Queue;
import javax.jms.Session;
import javax.jms.TextMessage;
import javax.jms.QueueSession;
import javax.jms.QueueReceiver;
import javax.jms.QueueConnection;
import javax.jms.QueueConnectionFactory;
public class Receiver
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// get the initial context
InitialContext context = new InitialContext();
// lookup the queue object
Queue queue = (Queue) context.lookup("queue/queue0");
// lookup the queue connection factory
QueueConnectionFactory conFactory = (QueueConnectionFactory) context.lookup ("queue/connectionFactory");
// create a queue connection
QueueConnection queConn = conFactory.createQueueConnection();
// create a queue session
QueueSession queSession = queConn.createQueueSession(false,
Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
// create a queue receiver
QueueReceiver queReceiver = queSession.createReceiver(queue);
// start the connection
queConn.start();
// receive a message
TextMessage message = (TextMessage) queueReceiver.receive();
// print the message
System.out.println("Message Received: " + message.getText());
// close the queue connection
queConn.close();
}
}
In the above code the receiver will receive the message from the sender and print it i.e. Hello World. But if the connection is not started then the method receiver will be blocked till the time any other thread starts the connection.
Happy Learning !!

Comments