In an application, we create different classes and design their interactions. These classes may or may not be associated with other to simulate real-life entities.
Association, aggregation and composition are three types of relationships that classes can have in object-oriented programming. It is clear from the given image that aggregation and compositions are also specific types of association.
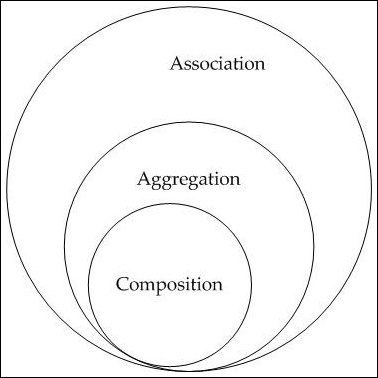
1. Association
Association is the most lenient relationship. The association refers to relationships whose participant objects have independent lifecycles and there is no ownership between the objects.
Let’s take an example of a Teacher and Student. A single student can be associated with multiple teachers, and a single teacher can teach multiple students, but both have their own lifecycles (both can be created and deleted independently).
For example, when a teacher leaves the school, we don’t need to remove any students, and when a student leaves the school, we don’t need to remove any teachers.
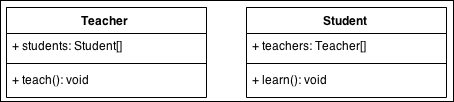
In the following code, Teacher and Student classes refer to each other but they are independent. Both classes can be modified without affecting the other class.
class Teacher {
List<Student> students;
public void teach(){
}
}
class Student {
List<Teacher> teachers;
public void learn(){
}
}Note that association can be one of the following types:
- one-to-one
- one-to-many
- many-to-one
- many-to-many
The discussed example of Student and Teacher
2. Aggregation
Aggregation is a little restrictive type of association. It refers to relationship between two classes such that objects of both classes can have independent lifecycle, but object of one class will belong to a specific object of the another class in its lifetime. It cannot belong to two objects of the same class.
To understand in real world terminology, let us take the example of a cell phone and battery. A battery can be associated with any phone, but once the relationship establishes, we cannot use a battery in two cell phones at the same time. The cell phone owns the battery when it is in use.
In technical terms, when we delete the phone from the database, the phone battery object will not be deleted because it may still be functional and can be used in another phone. So in aggregation, while there is ownership, objects have their own lifecycle.
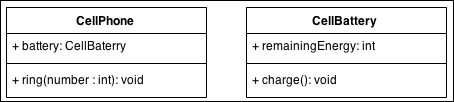
In the following code, CellPhone refers to an instance of CellBattery class. The same CellBattery instance cannot be used with other instances of CellPhone. Ideally, to get the instance of CellBattery, we must access it through the instance of CellPhone only.
class CellPhone {
CellBattery battery;
public void ring(){
}
}
class CellBattery {
short remainingEnergy;
public void charge(){
}
}To know the battery percentage, we must first access the CellPhone instance.
short remainingEnergy = phone.getBattery().getRemainingEnergy();3. Composition
Composition is the more strict relationship between two classes. It to refer to relationships where two objects don’t have an independent lifecycle, and if the parent object is deleted, all child objects will also be deleted.
Let’s take an example of the relationship between questions and answers. A multiple-choce question can have multiple answers. But an answer cannot belong to multiple questions. If we delete a question, its answers will automatically be deleted.
class Question {
int id;
String text;
List<Answer> answers;
}
class Answer {
long id;
String text;
boolean correct;
}4. Conclusion
Sometimes, deciding if the relationship is association, aggregation, or composition can be a complicated process. This difficulty is partly caused because aggregation and composition are subsets of association, meaning they are specific cases of association.
But with little focus and lessons learned in this tutorial, we can easily identify the differences between these relationships.
Drop me your questions in the comments section.
Happy Learning !!

Comments