In the Spring framework, the AOP module is one of the core components that enables important functionalities such as application auditing, transactional management, and security.
AOP is referred to as a tool for implementing cross-cutting concerns. The term crosscutting concerns refers to logic in an application that cannot be decomposed from the rest of the application and may result in code duplication and tight coupling. By using AOP for modularizing individual pieces of logic, known as concerns, you can apply them to many parts of an application without duplicating the code or creating hard dependencies.
Logging and security are typical examples of crosscutting concerns that are present in many applications. You often need to log actions or check if someone has permission in many parts of your program. AOP helps you do this without writing the same code all over the place.
1. What is Spring AOP?
Aspect-Oriented Programming is a paradigm that complements Object-Oriented Programming (OOP). While OOP is concerned with organizing code into classes and objects, AOP focuses on cross-cutting concerns – functionalities that affect multiple parts of an application. Cross-cutting concerns include logging, security, transactions, and more.
In the Spring framework, Spring AOP is a core module that provides a robust and elegant solution to address the challenges posed by cross-cutting concerns. It allows us to modularize these concerns thus enhancing code maintainability and reducing redundancy. Spring AOP seamlessly integrates with the Spring IoC (Inversion of Control) container, making it an integral part of the Spring ecosystem.
2. Spring AOP Architecture
The core architecture of Spring AOP is based on proxies. When the application is initialized, an advised instance of a class is created as the result of a ProxyFactory creating a proxy instance of that class with all the aspects woven into the proxy.
In runtime, Spring analyzes the crosscutting concerns defined for the beans in ApplicationContext and generates proxy beans (which wrap the underlying target bean) dynamically. Instead of accessing the target bean directly, callers are injected with the proxied bean.
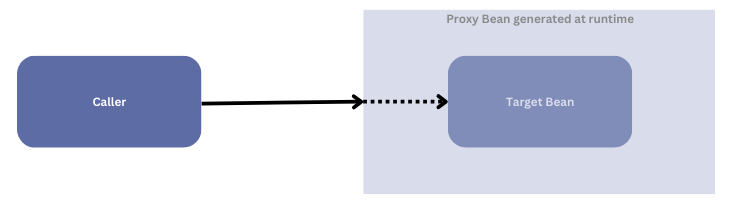
Internally, Spring has two proxy implementations:
- JDK dynamic proxies: when the target object to be advised implements an interface.
- CGLIB proxies: when the advised target object doesn’t implement an interface. For example, it’s a concrete class.
Note that the JDK dynamic proxy supports only the proxying of interfaces.
Remember that Spring AOP has some limitations. Such as:
- Final classes or methods cannot be proxied since they cannot be extended.
- Also, due to the proxy implementation, Spring AOP only applies to public, nonstatic methods on Spring Beans.
- If there is an internal method call from one method to another within the same class, the advice will never be executed for the internal method call.
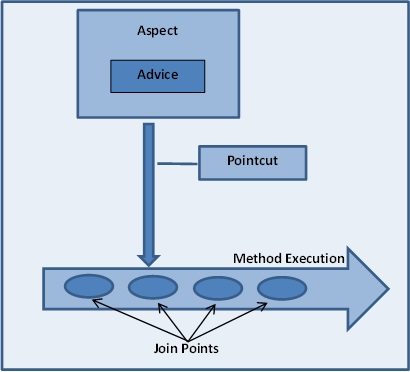
3. What is Advice, Joinpoint and Pointcut?
- Joinpoint: is a point of execution of the program, such as executing a method or handling an exception. In Spring AOP, a joinpoint always represents a method execution. Joinpoints define the points in your application at which you can insert additional logic using AOP.
- Advice: is the code that is executed at a particular joinpoint. There are many types of advice, such as before, which executes before the joinpoint, and after, which executes after it.
- Aspect: is the combination of advices and pointcuts encapsulated in a class.
- Pointcut: is a predicate or expression that matches joinpoints.
- Weaving: is the process of inserting aspects into the application code at the appropriate point. AspectJ supports a weaving mechanism called loadtime weaving (LTW), in which it intercepts the underlying JVM class loader and provides weaving to the bytecode when it is being loaded by the class loader.
- Target: is the object whose execution flow is modified by an AOP process. Often you see the target object referred to as the advised object.
- Spring uses the AspectJ pointcut expression language by default.
4. Types of Advice in Spring AOP
There are five types of advice in Spring AOP.
- Before advice: Advice that executes before a join point, but which does not have the ability to prevent execution flow proceeding to the join point (unless it throws an exception).
- After returning advice: Advice to be executed after a join point completes normally: for example, if a method returns without throwing an exception.
- After throwing advice: Advice to be executed if a method exits by throwing an exception.
- After advice: Advice to be executed regardless of the means by which a join point exits (normal or exceptional return).
- Around advice: Advice that surrounds a join point such as a method invocation. This is the most powerful kind of advice. Around advice can perform custom behavior before and after the method invocation. It is also responsible for choosing whether to proceed to the join point or to shortcut the advised method execution by returning its own return value or throwing an exception.
Choosing an advice type is based on the requirements of the application, but we should choose the most specific advice type for our needs. Don’t use around advice when before advice will do.
In most cases, around advice can accomplish everything that the other three advice types can, but it may be overkill for what you are trying to achieve. By keeping the advice type as focused as possible, we reduce the scope for errors.
5. Getting Started with Spring AOP
Let us peek into how to use AOP in a Spring application.
5.1. Maven
Before writing any code, you will need to import Spring AOP dependencies into your project.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>6.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>6.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>1.9.20.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.20.1</version>
</dependency>In a Spring Boot application, adding dependencies is rather easier.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
5.2. Enabling Spring AOP
We can enable Spring AOP using the @EnableAspectJAutoProxy annotation on a configuration.
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan
public class AopConfig {
}5.3. Define an Advice using Aspect and Pointcut Expression
Each Aspect class should be annotated with @Aspect annotation. Within that class, we then specify Pointcuts and Advice. It should also be annotated with @Component to be picked up by component scanning (or configured as a Spring bean in another way).
@Aspect
public class EmployeeCRUDAspect {
@Before("execution(* EmployeeManager.getEmployeeById(..))") //point-cut expression
public void logBeforeV1(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("EmployeeCRUDAspect.logBeforeV1() : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
}5.4. Advised Methods (Jointpoints)
Write methods on which you want to execute advice and those match with point-cut expressions.
@Component
public class EmployeeManager {
public EmployeeDTO getEmployeeById(Integer employeeId) {
System.out.println("Method getEmployeeById() called");
return new EmployeeDTO();
}
}In the above example, logBeforeV1() will be executed before getEmployeeById() method because it matches the join-point expression.
5.5. Run the Application
Run the application and watch the console.
public class TestAOP
{
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
("com/howtodoinjava/demo/aop/applicationContext.xml");
EmployeeManager manager = context.getBean(EmployeeManager.class);
manager.getEmployeeById(1);
}
}Program output:
EmployeeCRUDAspect.logBeforeV1() : getEmployeeById
Method getEmployeeById() calledSpring aop tutorial for beginners with example.
6. Spring AOP Annotation Examples
- Spring AOP AspectJ Annotation Configuration Example: Learn to configure AOP aspects using AspectJ annotations configuration
- Spring AOP AspectJ @Before: Learn to configure aop before the advice aspect using
@Beforeannotation. - Spring AOP AspectJ @After: Learn to configure aop after the advice aspect using
@Afterannotation. - Spring AOP AspectJ @Around: Learn to configure aop around the advice aspect using
@Aroundannotation. - Spring AOP AspectJ @AfterReturning: Learn to configure aop after returning advice aspect using
@AfterReturningannotation. - Spring AOP AspectJ @AfterThrowing: Learn to configure aop after throwing advice aspect using
@AfterThrowingannotation.
7. Spring AOP Advanced Tutorials
- Spring AOP Aspects Ordering: Learn to order the aspect execution in case of multiple aspects that need to be executed in a certain order.
- Spring AOP AspectJ Pointcut Expressions: Learn to write pointcut expressions to match a variety of joinpoints.
8. Spring AOP Interview Questions
- Top Spring AOP Interview Questions with Answers: Some most asked spring AOP interview questions in Java interviews.
Happy Learning !!
