Learn to write unit tests for the service layer of Spring boot applications using JUnit 5 and Mockito testing frameworks. We are using Spring Boot 3 in this demo. For Spring Boot applications, we only need to change the import statements, and everything should work automatically.
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
public class ItemServiceTest {
@Mock
private ItemRepository itemRepository;
@InjectMocks
private ItemService itemService; // Assuming ItemService uses ItemRepository
@Test
public void testCreateItem() {
// ...
}
}1. Maven
The spring-boot-starter-test dependency transitively imports JUnit 5 and Mockito. So we only need to include this dependency.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>2. Initializing Mocks
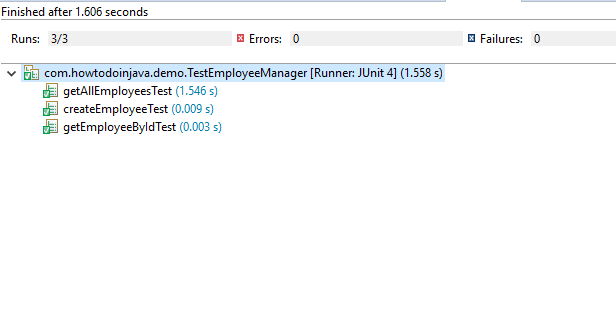
In this example, we are unit testing primarily two classes EmployeeManager and EmployeeDao. As the name implies, the manager class represents the service layer, and dao class interacts with the database.
The EmployeeManager class has a dependency on EmployeeDao to get the data from the database that is finally returned to controller classes. To test the methods in EmployeeManager, we can create a JUnit test class TestEmployeeManager in below given two ways:
2.1. @Mock vs @InjectMocks
- The @Mock annotation creates a mock implementation for the class it is annotated with.
- @InjectMocks also creates the mock implementation of annotated type and injects the dependent mocks into it.
In the above example, we have annotated EmployeeManager class with @InjectMocks, so mockito will create the mock object for EmployeeManager class and inject the mock dependency of EmployeeDao into it.
2.2. Initialization with MockitoExtension
To process Mockito annotations with JUnit, we need to use MockitoExtention which automatically initializes all the objects annotated with @Mock and @InjectMocks annotations.
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
public class TestEmployeeManager {
@InjectMocks
EmployeeManager manager;
@Mock
EmployeeDao dao;
//tests
}2.3. Initialization with MockitoAnnotations.openMocks()
If we are not using the MockitoJUnitRunner class approach, then we can use the static method MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(). Upon initialization of junit tests, this method also initializes the mock objects.
The previously used MockitoAnnotations.initMocks() method has been deprecated and should not be used.
public class ServiceTests {
@InjectMocks
EmployeeService service;
@Mock
EmployeeRepository dao;
@BeforeEach
public void init() {
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
}
//tests
}3. Sprig Boot Tests
Let’s see a few examples of writing the junit tests to unit test the service layer and DAO layer methods using mock objects created with mockito.
A few example methods could be for getAllEmployees() returning a list of EmployeeVO objects, getEmployeeById(int id) for returning an employee by given id; and createEmployee() for adding an employee object and return void.
3.1. Unit Tests Example
The following class contains the tests for service class methods. It uses Mockito.when() methods to create test stubs.
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.times;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.verify;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.mockito.InjectMocks;
import org.mockito.Mock;
import org.mockito.MockitoAnnotations;
import org.mockito.junit.jupiter.MockitoExtension;
import com.howtodoinjava.employees.dao.EmployeeRepository;
import com.howtodoinjava.employees.model.Employee;
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
public class ServiceTests {
@InjectMocks
EmployeeService service;
@Mock
EmployeeRepository dao;
@Test
void testFindAllEmployees() {
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<Employee>();
Employee empOne = new Employee("John", "John");
Employee empTwo = new Employee("Alex", "kolenchiski");
Employee empThree = new Employee("Steve", "Waugh");
list.add(empOne);
list.add(empTwo);
list.add(empThree);
when(dao.findAll()).thenReturn(list);
//test
List<Employee> empList = service.findAll();
assertEquals(3, empList.size());
verify(dao, times(1)).findAll();
}
@Test
void testCreateOrSaveEmployee() {
Employee employee = new Employee("Lokesh", "Gupta");
service.save(employee);
verify(dao, times(1)).save(employee);
}
}Please note that Mockito throws an UnsupportedStubbingException when an initialized mock is not called during test execution. If there are such optional mocked behavior then use Mockito.lenient() as follows:
Mockito.lenient().when(dao.isEmployeeDeleted()).thenReturn(Boolean.False);3.2. Service Class to Be Mocked
For reference, the service class is as follows:
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
@Autowired
EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
public Employee save(Employee employee) {
//...
}
public List<Employee> findAll() {
//...
}
public void deleteById(Integer id) {
//...
}
void deleteAll() {
//...
}
}3.3. Dao Layer to Be Injected
Also, for reference, the DAO class is as follows:
@Repository
public interface EmployeeRepository extends CrudRepository<Employee, Integer> {
}4. Conclusion
This mockito tutorial taught us to unit test the service layer in spring boot applications using JUnit and Mockito. We learned to set up the test class and to write JUnit tests. We also learned the difference between @Mock and @InjectMocks annotations.
Happy Learning !!

Comments