This is a very common interview question. We are asked if we have a linked list in which we can traverse only in one direction and if that linked list has a loop in it, how will we detect it??
Well, if you don’t know the answer then don’t be demoralized. My personal opinion is that this kind of question does not evaluate the logical thinking of a candidate because problems like this have a very specific answer. Either you know it, or you don’t.
1. Finding Infinite Loop in LinkedList
For this specific question, the best answer the interviewer is looking for is “Floyd's Cycle-Finding Algorithm“. This algorithm suggests a solution in which instead of only one pointer to traverse through a list, we are advised to have two pointers at a time. Both pointers will start from the first node of the linked list and traverse using the next attribute.
The difference lies in the number of nodes that they jump in each step. First node jump to the next node each time, whereas another node jumps two nodes at a time. The first node is called the slower node or “tortoise“, and the second faster node is called “hare“.
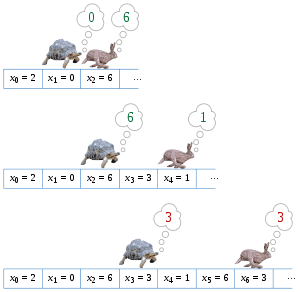
This traversal ensures that if there is a loop in linked list then both the nodes will meet somewhere in their traversal path for sure. It has O(n) complexity.
2. Demo
Let us verify this using a Java program. I have written the least possible single linked list code for demonstration of this example only.
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.core;
public class SinglyLinkedList {
private Node start;
public void add(Integer i)
{
Node node = new Node(i);
if(start == null)
start = node;
else
{
Node temp = start;
while(temp.next != null)
{
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = node;
}
}
public Node getStart()
{
return start;
}
static class Node
{
Node(Integer i)
{
this.value = i;
}
private Integer value;
private Node next;
public Integer getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(Integer value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
}Now, let’s test the above linked list first without a loop and then with a loop inside it. We are using createLoop() to insert the infinite loop in the list.
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.core;
public class FindLoopsInLinkedList
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
FindLoopsInLinkedList finder = new FindLoopsInLinkedList();
SinglyLinkedList sampleList = new SinglyLinkedList();
// First Insert randomly ten elements in a linked list
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
sampleList.add(i);
}
System.out.println("Loop Existence : " + finder.doesLoopExist(sampleList));
System.out.println("Loop Existence : " + finder.doesLoopExist(finder.createLoop(sampleList)));
}
public boolean doesLoopExist(SinglyLinkedList listToCheck) {
SinglyLinkedList.Node tortoise = listToCheck.getStart();
SinglyLinkedList.Node hare = listToCheck.getStart();
try {
while (true) {
tortoise = tortoise.getNext();
hare = hare.getNext().getNext();
if (tortoise == hare) {
return true;
}
}
} catch (NullPointerException ne) {
return false;
}
}
private SinglyLinkedList createLoop(SinglyLinkedList sampleList) {
sampleList.getStart().getNext().getNext().getNext().setNext(sampleList.getStart().getNext());
return sampleList;
}
}In the above program, we have created a linked list and then inserted 10 elements in this list. No, when we checked the loop presence in line no. 15 it comes as false.
But, when in line 167, we have created a loop inside linked list result comes as true.
The output of the above program is this:
Loop Existence : false [Line 15]
Loop Existence : true [Line 16]As you see, as soon as we insert a loop in line no. 16, our algorithm implementation is able to detect it.
Happy Learning !!

Comments