The while loop in Java continually executes a block of statements until a particular condition evaluates to true. As soon as the condition becomes false, the while loop terminates.
As a best practice, if the number of iterations is not known at the start, it is recommended to use the while loop.
1. Syntax
The syntax of while loop is:
while (condition-expression) {
statement(s);
}The condition-expression must be a boolean expression and the statements can be one simple statement or a block of multiple statements. Every time the condition-expression evaluates to true, statement(s) block is executed.
The while statement continues testing the condition-expression in loop and executing the block until the condition-expression evaluates to false.
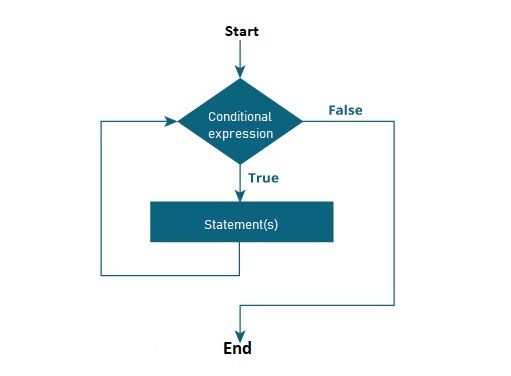
- The execution starts with the evaluation of the
condition-expression. - If the condition is evaluated to
true,statementsblock is executed. This is called an iteration. - An iteration happens everytime the condition is
true. - When the condition is evaluated to
false, the loop is terminated immediately.
2. While Loop Example
Let us understand the while loop with a few examples.
2.1. Print all numbers from 1 to N
To print all integers between 1 and 5 using a while-loop, we can create a condition on a local variable counter that must not be less than or equal to 5.
As soon as, the counter reaches 6, the loop terminates.
int counter = 1;
while (counter <= 5) {
System.out.println(counter);
counter++;
}Program output.
1
2
3
4
52.2. Iterate through a List
The following Java program iterates over an ArrayList using its iterator in the while loop.
List<String> list = List.of("A", "B", "C");
Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}Program output.
A
B
C2.3. Iterate through an Array
To iterate over array, we should create the condition on array length. We need to iterate over all array elements using the index counter.
Once index reaches is equal to the length of the array, the while loop terminates.
Integer[] array = new Integer[] {1,2,3,4,5};
int index = 0;
while (index < array.length) {
System.out.println(array[index]);
index++;
}Program output.
1
2
3
4
53. Infinite While Loop
Programmers makes mistake. If the conditional-expression given in while loop never terminates then the loop will result in an infinite while-loop. For example, in the previous program, if the index value is not incremented after each iteration, then the condition will never terminate.
In the next example, index start with 0 and check if it is less than the array length. As we are not incrementing its value, it will always be less than 5, no matter how many iterations happen. This loop is an infinite loop.
Integer[] array = new Integer[] {1,2,3,4,5};
int index = 0;
while (index < array.length) //Infinite Loop because we are not incrementing the index
{
System.out.println(array[index]);
}The infinite loops, sometimes, result into StackOverflowError or OutOfMemoryError based on what we are trying to do in the loop. If there are no memory leaks, it is possible that the loop never terminates and executes infinitely. The program will hang in this situation.
4. Difference between While-loop and For-loop
Unlike the for-loop statement, the condition-expression in while loop statement is not optional. In general, a for-loop statement can be converted to a while-loop statement. However, not all for-loop statements can be converted to a while-loop statement.
The following is a pseudo-code for writing a simple for loop.
for (initialization; condition-expression; expression-list) {
statements;
}We can write the equivalent program using the while loop as follows:
initialization;
while (condition-expression)
{
statements;
expression-list;
}5. While loop with break Keyword
A break statement is used to exit the loop in a while-loop statement. It is helpful in terminating the loop if a certain condition evaluates during the execution of the loop body.
int i = 1;
while (true) // Cannot exit the loop from here
{
if (i <= 5) {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
} else {
break; // Exit the loop
}
}Simple, right? Practice it more by creating a few more programs around while loop statement.
Happy Learning !!


Comments