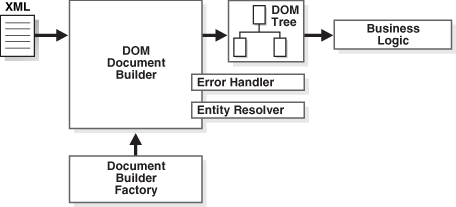
In this Java xml parser tutorial, learn to read XML using DOM parser. DOM parser is intended for working with XML as an object graph (a tree-like structure) in memory – the so-called “Document Object Model (DOM)“.
At first, the parser traverses the input XML file and creates DOM objects corresponding to the nodes in the XML file. These DOM objects are linked together in a tree-like structure. Once the parser is done with the parsing process, we get this tree-like DOM object structure back from it. Now we can traverse the DOM structure back and forth as we want – to get/update/delete data from it.
The other possible ways to read an XML file are using the SAX parser and StAX parser as well.
1. Setup
For demo purposes, we will be parsing the below XML file in all code examples.
<employees>
<employee id="111">
<firstName>Lokesh</firstName>
<lastName>Gupta</lastName>
<location>India</location>
</employee>
<employee id="222">
<firstName>Alex</firstName>
<lastName>Gussin</lastName>
<location>Russia</location>
</employee>
<employee id="333">
<firstName>David</firstName>
<lastName>Feezor</lastName>
<location>USA</location>
</employee>
</employees>2. DOM Parser API
Let’s note down some broad steps to create and use a DOM parser to parse an XML file in java.
1.1. Import dom Parser Packages
We will need to import dom parser packages first in our application.
import org.w3c.dom.*;
import javax.xml.parsers.*;
import java.io.*;1.2. Create DocumentBuilder
The next step is to create the DocumentBuilder object.
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();1.3. Create Document object from XML file
Read the XML file to Document object.
Document document = builder.parse(new File( file ));1.4. Validate Document Structure
XML validation is optional but good to have it before starting parsing.
Schema schema = null;
try {
String language = XMLConstants.W3C_XML_SCHEMA_NS_URI;
SchemaFactory factory = SchemaFactory.newInstance(language);
schema = factory.newSchema(new File(name));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackStrace();
}
Validator validator = schema.newValidator();
validator.validate(new DOMSource(document));1.5. Extract the Root Element
We can get the root element from the XML document using the below code.
Element root = document.getDocumentElement();1.6. Examine Attributes
We can examine the XML element attributes using the below methods.
element.getAttribute("attributeName") ; //returns specific attribute
element.getAttributes(); //returns a Map (table) of names/values1.7. Examine Child-Elements
Child elements for a specified Node can be inquired about in the below manner.
node.getElementsByTagName("subElementName"); //returns a list of sub-elements of specified name
node.getChildNodes(); //returns a list of all child nodes2. Read XML File with DOM parser
In the below example code, we are assuming that the user is already aware of the structure of employees.xml file (its nodes and attributes). So example directly starts fetching information and starts printing it in the console. In a real-life application, we will use this information for some real purpose rather than just printing it on the console and leaving.
public static Document readXMLDocumentFromFile(String fileNameWithPath) throws Exception {
//Get Document Builder
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
//Build Document
Document document = builder.parse(new File(fileNameWithPath));
//Normalize the XML Structure; It's just too important !!
document.getDocumentElement().normalize();
return document;
}Now we can use this method to parse the XML file and verify the content.
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Document document = readXMLDocumentFromFile("c:/temp/employees.xml");
//Verify XML Content
//Here comes the root node
Element root = document.getDocumentElement();
System.out.println(root.getNodeName());
//Get all employees
NodeList nList = document.getElementsByTagName("employee");
System.out.println("============================");
for (int temp = 0; temp < nList.getLength(); temp++) {
Node node = nList.item(temp);
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
//Print each employee's detail
Element eElement = (Element) node;
System.out.println("\nEmployee id : " + eElement.getAttribute("id"));
System.out.println("First Name : " + eElement.getElementsByTagName("firstName").item(0).getTextContent());
System.out.println("Last Name : " + eElement.getElementsByTagName("lastName").item(0).getTextContent());
System.out.println("Location : " + eElement.getElementsByTagName("location").item(0).getTextContent());
}
}
}Program Output:
employees
============================
Employee id : 111
First Name : Lokesh
Last Name : Gupta
Location : India
Employee id : 222
First Name : Alex
Last Name : Gussin
Location : Russia
Employee id : 333
First Name : David
Last Name : Feezor
Location : USA3. Read XML into POJO
Another real-life application’s requirement might be populating the DTO objects with information fetched in the above example code. I wrote a simple program to help us understand how it can be done easily.
Let’s say we have to populate Employee objects which are defined as below.
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String location;
//Setters, Getters and toString()
}Now, look at the example code to populate the Employee objects list. It is just as simple as inserting a few lines in between the code, and then copying the values in DTOs instead of the console.
public static List<Employee> parseXmlToPOJO(String fileName) throws Exception {
List<Employee> employees = new ArrayList<Employee>();
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
Document document = builder.parse(new File(fileName));
document.getDocumentElement().normalize();
NodeList nList = document.getElementsByTagName("employee");
for (int temp = 0; temp < nList.getLength(); temp++) {
Node node = nList.item(temp);
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element eElement = (Element) node;
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(Integer.parseInt(eElement.getAttribute("id")));
employee.setFirstName(eElement.getElementsByTagName("firstName").item(0).getTextContent());
employee.setLastName(eElement.getElementsByTagName("lastName").item(0).getTextContent());
employee.setLocation(eElement.getElementsByTagName("location").item(0).getTextContent());
//Add Employee to list
employees.add(employee);
}
}
return employees;
}4. Parse “unknown” XML using NamedNodeMap
The previous example shows how we can iterate over an XML document parsed with known or little know structure to you, while you are writing the code. In some cases, we may have to write the code in such a way that even if there are some differences in the assumed XML structure while coding, the program must work without failure.
Here we are iterating over all elements present in the XML document tree. we can add our knowledge and modify the code such that as soon as we get the required information while traversing the tree, we just use it.
private static void visitChildNodes(NodeList nList) {
for (int temp = 0; temp < nList.getLength(); temp++) {
Node node = nList.item(temp);
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
System.out.println("Node Name = " + node.getNodeName() + "; Value = " + node.getTextContent());
//Check all attributes
if (node.hasAttributes()) {
// get attributes names and values
NamedNodeMap nodeMap = node.getAttributes();
for (int i = 0; i < nodeMap.getLength(); i++) {
Node tempNode = nodeMap.item(i);
System.out.println("Attr name : " + tempNode.getNodeName() + "; Value = " + tempNode.getNodeValue());
}
if (node.hasChildNodes()) {
//We got more children; Let's visit them as well
visitChildNodes(node.getChildNodes());
}
}
}
}
}Program Output.
employees
============================
Node Name = employee; Value =
Lokesh
Gupta
India
Attr name : id; Value = 111
Node Name = firstName; Value = Lokesh
Node Name = lastName; Value = Gupta
Node Name = location; Value = India
Node Name = employee; Value =
Alex
Gussin
Russia
Attr name : id; Value = 222
Node Name = firstName; Value = Alex
Node Name = lastName; Value = Gussin
Node Name = location; Value = Russia
Node Name = employee; Value =
David
Feezor
USA
Attr name : id; Value = 333
Node Name = firstName; Value = David
Node Name = lastName; Value = Feezor
Node Name = location; Value = USAThat’s all for this good-to-know concept around Java XML DOM Parser. Drop me a comment if something is not clear OR needs more explanation.
Happy Learning !!


Comments