Date and time handling has always been a pain area for Java developers. The new Date-Time API added in Java 8 changed the way, we interact with date and time in Java.
New Date API is a very powerful and much-needed improvement. The only thing missing was, getting a stream of dates having some common difference between two subsequent dates (though it was possible there was no easy way).
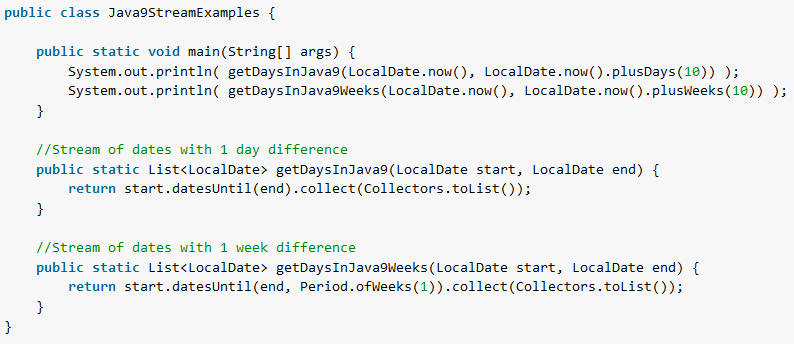
Java 9 has introduced a new method LocalDate.datesUntil() that can give a stream on dates. Using datesUntil() makes it easy to create dates streams with a fixed offset.
1. LocalDate.datesUntil() Method (Java 9)
1.1. Syntax
This method has two overloaded forms:
startDate.datesUntil(endDate): returns a sequential ordered stream of dates that starts fromstartDate(inclusive) and goes toendDate(exclusive) by an incremental step of 1 day.startDate.datesUntil(endDate, period): same as above with a configured incremental stepperiod.
Stream<LocalDate> datesUntil(LocalDate end)
Stream<LocalDate> datesUntil(LocalDate end, Period step)1.2. Example of Stream of Dates
Creating a stream of dates is very simple and straightforward as demonstrated in the given examples.
In this example, we are getting the dates for the next 3 consecutive days.
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
Stream<LocalDate> next3Days = today.datesUntil(today.plusDays(3));
next3Days.forEach(System.out::println);In the next example, we are getting the same day for the next 3 weeks.
Stream<LocalDate> sameDayNext3Weeks = today
.datesUntil(today.plusDays(21), Period.ofWeeks(1));
sameDayNext3Weeks.forEach(System.out::println);2. Get Stream of Dates using Iteration (Java 8)
If you have still not adapted Java 9, then you can use the given below method to generate date streams.
Stream<LocalDate> nextThreeDays = Stream.iterate(today, d -> d.plusDays(1));Once we have the stream, we can use the stream operations on the items.
Stream<LocalDate> nextThreeDays = Stream.iterate(today, d -> d.plusDays(1));
List<LocalDate> list = nextThreeDays
.limit(3)
.collect(Collectors.toList());Happy Learning !!

Comments