Learn to create HTTP POST REST APIs using Spring boot which accepts a JSON request and returns a JSON response to the API consumer.
1. Maven
First, create a simple maven web project and update the following starter dependency in pom.xml file.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>2. REST Controller
In Spring, a controller class, which is capable of serving REST API requests, is called the rest controller. It should be annotated with @RestController annotation. In the given rest controller, we have two API methods. Feel free to add more methods as needed.
The POST API is for creating a new Employee in the system.
- It adds an employee to the application.
- It accepts employee data in
Employeeobject. - It accepts and creates JSON media types.
- It accepts two HTTP headers i.e. X-COM-PERSIST and X-COM-LOCATION. The first header is required and the second header is optional. These custom headers can be used to control how the employee data is saved in the system.
- It returns the location of the resource created.
@RestController
@RequestMapping(path = "/employees")
public class EmployeeController
{
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
@PostMapping(path= "/", consumes = "application/json", produces = "application/json")
public ResponseEntity<Object> addEmployee(
@RequestHeader(name = "X-COM-PERSIST", required = true) String headerPersist,
@RequestHeader(name = "X-COM-LOCATION", required = false, defaultValue = "ASIA") String headerLocation,
@RequestBody Employee employee) throws Exception
{
//validate the employee data if required
//add resource to database
Employee createdEmployee = employeeRepository.addEmployee(employee);
//Create resource location
URI location = ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentRequest()
.path("/{id}")
.buildAndExpand(createdEmployee.getId())
.toUri();
return ResponseEntity.created(location).build();
}
}3. Error Handling
A well-designed REST API must have consistent error messages as well. One way to achieve it in spring boot applications is using @ControllerAdvice or @RestControllerAdvice. Inside @ControllerAdvice annotated class, use @ExceptionHandler annotated methods to return consistent responses in invalid scenarios.
@ControllerAdvice
public class ApplicationExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ServletRequestBindingException.class)
public final ResponseEntity<Object> handleHeaderException(Exception ex, WebRequest request) {
List<String> details = new ArrayList<>();
details.add(ex.getLocalizedMessage());
ErrorResponse error = new ErrorResponse("Bad Request", details);
return new ResponseEntity(error, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public final ResponseEntity<Object> handleAllExceptions(Exception ex, WebRequest request) {
List<String> details = new ArrayList<>();
details.add(ex.getLocalizedMessage());
ErrorResponse error = new ErrorResponse("Server Error", details);
return new ResponseEntity(error, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}4. Request Validation
REST APIs also must have a mechanism to validate if the request body contains all the necessary information to create the resource in the server. We can use Spring Boot’s inbuilt support for Jakarta Validations for this purpose.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>To add validation of a request body, annotate the request input object with @Valid annotation in the handler method.
@PostMapping(path= "/", consumes = "application/json", produces = "application/json")
public ResponseEntity<Object> addEmployee(..., @Valid @RequestBody Employee employee) throws Exception
{
//...
}Next, we can add the JSR 380 annotation in the model class to add the validation rules specific to the fields. In runtime, the validation rules will be applied and MethodArgumentNotValidException will be thrown if it is an invalid request. We can catch this exception in the controller advice and return an appropriate response.
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ApplicationExceptionHandler {
//...
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(MethodArgumentNotValidException ex) {
List<String> details = new ArrayList<>();
for (ObjectError error : ex.getBindingResult().getAllErrors()) {
details.add(error.getDefaultMessage());
}
ErrorResponse error = new ErrorResponse("Validation Failed", details);
return new ResponseEntity(error, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
}5. Demo
To start the application, run the main() method in SpringBootDemoApplication class. It will start the embedded Tomcat server. In server logs, you will see that API has been registered in the spring context.
s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/employees/],methods=[GET],produces=[application/json]}" onto public com.howtodoinjava.rest.model.Employees com.howtodoinjava.rest.controller. EmployeeController.getEmployees()
s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped "{[/employees/],methods=[POST], consumes=[application/json], produces=[application/json]}" onto public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity <java.lang.Object> com.howtodoinjava.rest. controller. EmployeeController.addEmployee( java.lang.String, java.lang.String, com.howtodoinjava.rest.model.Employee) throws java.lang.Exception5.1. Validate Custom Headers
Once the server is UP, access the API using some rest client. Do not pass the request headers.
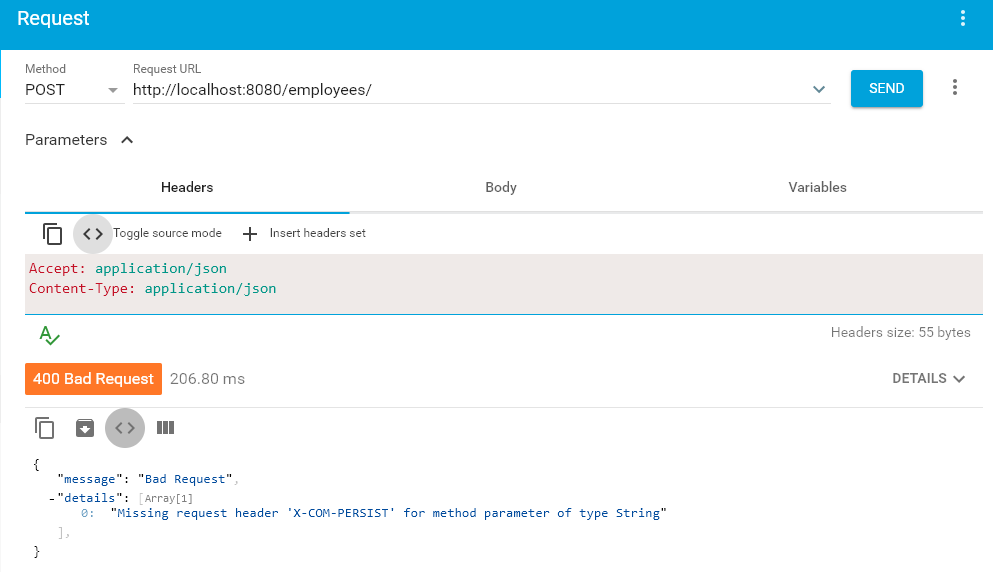
{
"message": "Bad Request",
"details": [
"Missing request header 'X-COM-PERSIST' for method parameter of type String"
],
}6.2. Successful Response
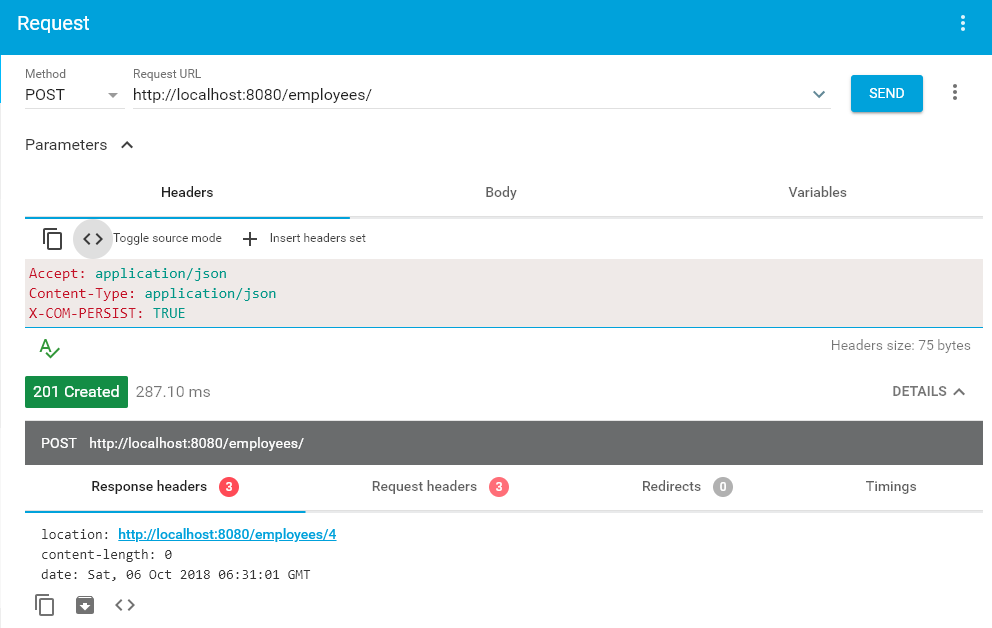
location: http://localhost:8080/employees/4
content-length: 0
date: Sat, 06 Oct 2018 04:33:37 GMTHit the GET request and this time we will get the added employee as well.

Let me know if you have a query in this spring boot post request example.
Happy Learning !!

Comments