AbstractRoutingDataSource is a very useful feature if we have a design which permits multiple databases based on certain criteria which may change for each user request. An example can be when we can use a particular database when the user belongs to a certain locale and switch to another locale if the user belongs to another locale.
AbstractRoutingDataSourceis an abstract data source implementation that routesgetConnection()calls to one of the various target DataSources based on a lookup key. The latter is usually (but not necessarily) determined through some thread-bound transaction context.
Lets see an example to use AbstractRoutingDataSource for selecting the appropriate data source for users based on their locale.
In the given example, we have configured only two locales “en” and “es”. We can configure as many data sources as we may like. Also, the locale is not only the only criteria for changing data sources. If you have some other requirements, feel free to add your own logic.
AbstractRoutingDataSource Example
1.1. Extend AbstractRoutingDataSource
This is required because here we will decide which datasource we want to go for in which condition.
package com.howtodoinjava.controller;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
public class MyRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
String language = LocaleContextHolder.getLocale().getLanguage();
System.out.println("Language obtained: "+ language);
return language;
}
}
1.2. Configure the datasources
Configure various data sources first, without worrying how they will be accessed.
<bean id="abstractDataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"
destroy-method="close"
p:driverClassName="${jdbc.driverClassName}"
p:username="${jdbc.username}"
p:password="${jdbc.password}" />
<bean id="concreteDataSourceOne"
parent="abstractDataSource"
p:url="${jdbc.databaseurlOne}"/>
<bean id="concreteDataSourceTwo"
parent="abstractDataSource"
p:url="${jdbc.databaseurlTwo}"/>
1.3. Setup the routing
Here we will actually define key-value pairs [“targetDataSources”] for all configured data sources in above step. The value will be data source bean name, and key will be result came from determineCurrentLookupKey() method in MyRoutingDataSource.
We can also mention a default data source if nothing can be found for any user request. If will be default one and prevent from exceptions.
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.howtodoinjava.controller.MyRoutingDataSource"> <property name="targetDataSources"> <map key-type="java.lang.String"> <entry key="en" value-ref="concreteDataSourceOne"/> <entry key="es" value-ref="concreteDataSourceTwo"/> </map> </property> <!-- <property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="concreteDataSourceOne"/> --> </bean>
1.4. Spring Configuration
<bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> <!-- HERE -->
<property name="configLocation">
<value>classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml</value>
</property>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">${jdbc.dialect}</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
After all changes your spring configuration will look like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xmlns:lang="http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang/spring-lang.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
<context:annotation-config />
<context:component-scan base-package="com.howtodoinjava.controller" />
<bean id="jspViewResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="viewClass"
value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView" />
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/view/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
<bean id="propertyConfigurer"
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"
p:location="/WEB-INF/jdbc.properties" />
<!-- Step 3 -->
<bean id="abstractDataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"
destroy-method="close"
p:driverClassName="${jdbc.driverClassName}"
p:username="${jdbc.username}"
p:password="${jdbc.password}" />
<bean id="concreteDataSourceOne"
parent="abstractDataSource"
p:url="${jdbc.databaseurlOne}"/>
<bean id="concreteDataSourceTwo"
parent="abstractDataSource"
p:url="${jdbc.databaseurlTwo}"/>
<!-- Step 4 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.howtodoinjava.controller.MyRoutingDataSource">
<property name="targetDataSources">
<map key-type="java.lang.String">
<entry key="en" value-ref="concreteDataSourceOne"/>
<entry key="es" value-ref="concreteDataSourceTwo"/>
</map>
</property>
<!-- <property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="concreteDataSourceOne"/> -->
</bean>
<bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource"
p:basenames="messages" />
<!-- Declare the Interceptor -->
<mvc:interceptors>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor"
p:paramName="locale" />
</mvc:interceptors>
<!-- Declare the Resolver -->
<bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver" />
<bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="configLocation">
<value>classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml</value>
</property>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">${jdbc.dialect}</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="employeeDAO" class="com.howtodoinjava.dao.EmployeeDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="employeeManager" class="com.howtodoinjava.service.EmployeeManagerImpl"></bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean>
</beans>
2. Demo
Before testing the application, we have created two database schemas and two similar tables in them. Both tables are exactly same except the data inside them. I have kept it different intentionally to demonstrate that two different requests are actually hitting different databases.
delimiter $$
CREATE DATABASE 'test' /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET latin1 */$$
USE test$$
CREATE TABLE 'employee' (
'ID' int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
'FIRSTNAME' varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
'LASTNAME' varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
'TELEPHONE' varchar(15) DEFAULT NULL,
'EMAIL' varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
'CREATED' timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY ('ID')
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1$$
INSERT INTO 'test'.'employee' ('ID','FIRSTNAME','LASTNAME','TELEPHONE','EMAIL','CREATED')
VALUES (4,'Lokesh','Gupta','9811111111','[email protected]',CURRENT_TIMESTAMP);
CREATE DATABASE 'testtwo' /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET latin1 */$$
USE testtwo$$
CREATE TABLE 'employee' (
'ID' int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
'FIRSTNAME' varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
'LASTNAME' varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
'TELEPHONE' varchar(15) DEFAULT NULL,
'EMAIL' varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
'CREATED' timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY ('ID')
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1$$
INSERT INTO 'testtwo'.'employee' ('ID','FIRSTNAME','LASTNAME','TELEPHONE','EMAIL','CREATED')
VALUES (1,'Rakesh','Shukla','1234','email',CURRENT_TIMESTAMP);
1) Hit the URL: http://localhost:8080/Spring3.2.5Hibernate4.0.1Integration/?locale=en
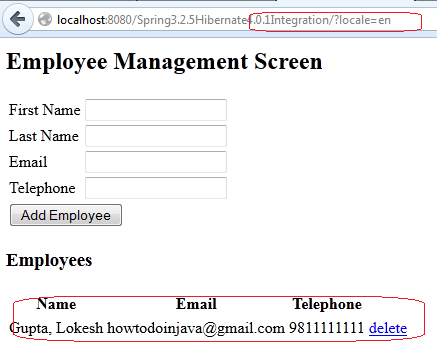
2) Hit the URL: http://localhost:8080/Spring3.2.5Hibernate4.0.1Integration/?locale=es
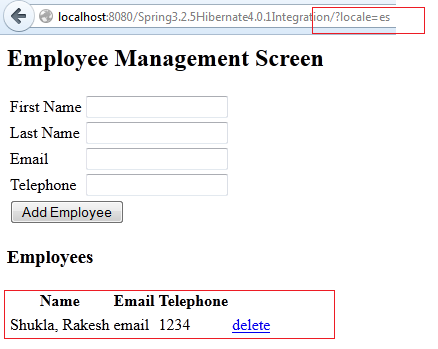
3) Hit the URL: http://localhost:8080/Spring3.2.5Hibernate4.0.1Integration/?locale=fr
This will cause an exception because we have neither setup any data source for this locale nor any default datasource [commented lines].
HTTP Status 500 - Request processing failed; nested exception is org.springframework.transaction.CannotCreateTransactionException: Could not open Hibernate Session for transaction; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalStateException: Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [fr] type Exception report message Request processing failed; nested exception is org.springframework.transaction.CannotCreateTransactionException: Could not open Hibernate Session for transaction; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalStateException: Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [fr]
Drop me a comment if something needs more explanation.
Happy Learning !!


Comments