Quicksort is a sorting algorithm that follows the divide-and-conquer approach. It works by dividing the input array into two sub-arrays, then recursively sorting each sub-array independently, and finally combining the sorted sub-arrays. In this article, we will discuss the implementation, complexity, advantages and disadvantages of the quicksort algorithm.
1. Quicksort Algorithm
The Quicksort algorithm sorts the elements in place, which means it doesn’t require any additional memory allocation to sort the data, and also it can handle large datasets efficiently.
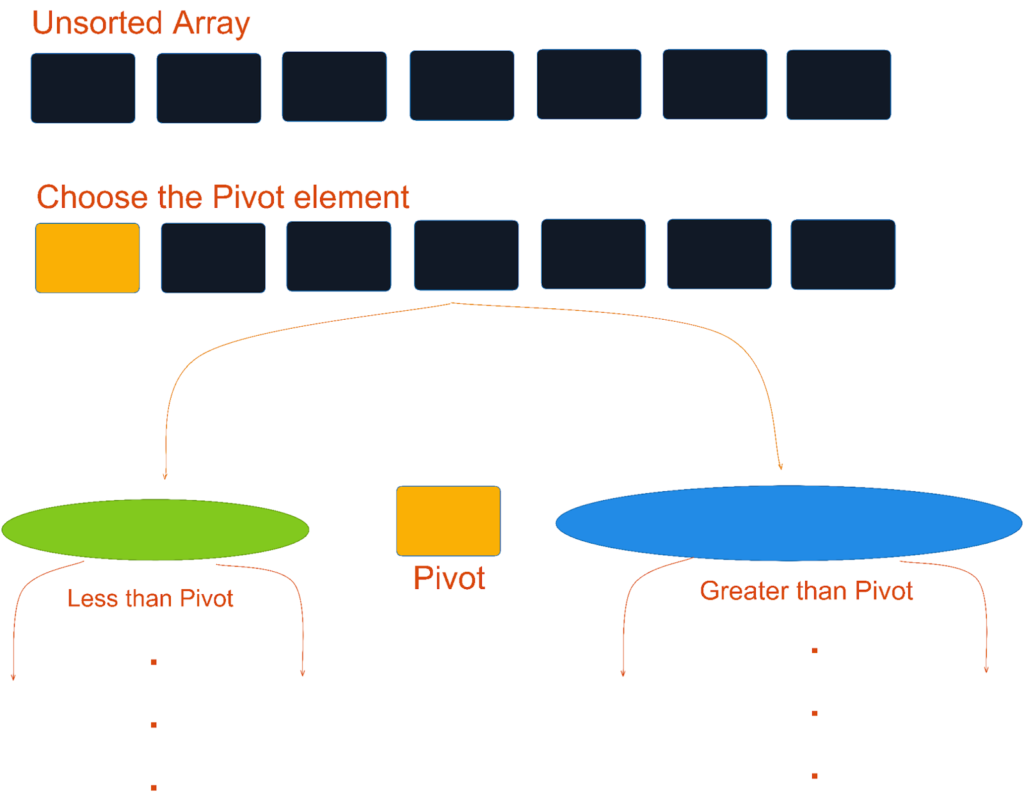
Let us see how Quicksort works:
- First, choose an element from the array. This element is called the pivot. The pivot can be any element in the list of data, but for simplicity, we usually choose the first or last element in the array.
- After choosing the pivot element, divide the array into two sub-arrays, with all the elements less than the pivot on one side and all the elements greater than the pivot on the other. This process of dividing is called partitioning.
- Recursively repeat the above step for each of the sub-arrays. Choose a pivot for each sub-array, partition it, and then sort the sub-arrays.
- Finally, combine all the sorted sub-arrays to get the final sorted array.
2. Quicksort in Action
Suppose we have the following array:
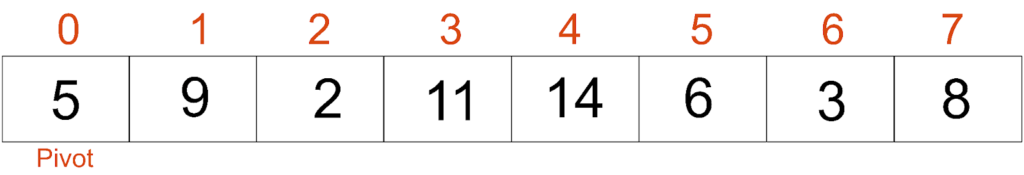
In quicksort, the first step is to select a pivot element, which is used to divide the array into two sub-arrays. For simplicity, let’s choose the first element as the pivot of the given array, which is 5.
Next, we partition the array into two sub-arrays: one with elements less than the pivot and the other with elements greater than the pivot. Note that if this array were sorted, the position of the pivot element (5) would be 2 (assuming zero-based indexing).
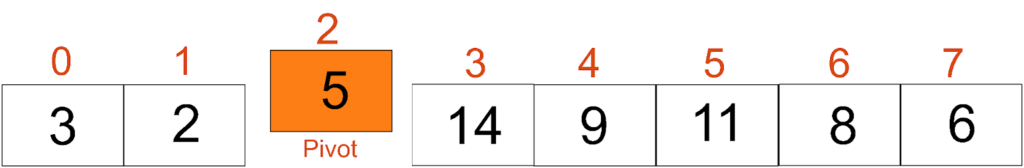
Now we recursively apply the same process to both sub-arrays. This is where the divide-and-conquer approach comes in, as we are dividing our larger problems into smaller ones.
For the first sub-array, we have two elements (3 and 2). Here, the pivot element would be 3. After positioning element 3 in its correct place, our array becomes [2, 3]. If we divide this sub-array again, it will divide into two single-size elements, i.e. [2] and [3], which are both base cases (In quicksort, a base case is when the sub-array to be sorted has 0 or 1 element). 2, 3, and 5 are at correct positions 0, 1, and 2.
For the second sub-array, the pivot element would be 14.
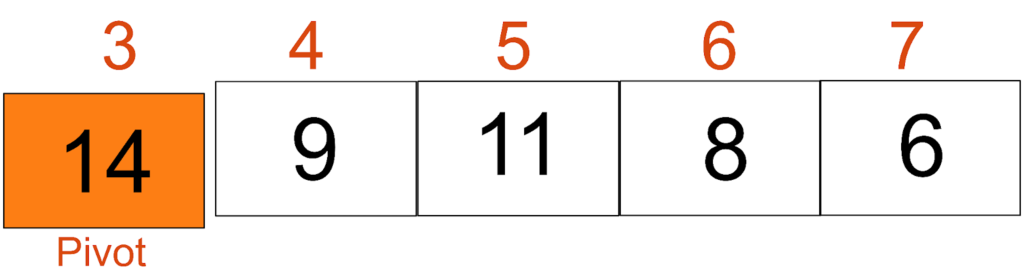
The pivot element, 14, will take its position. Since it is the largest element in the array, it will move to the last position as shown in the image below.
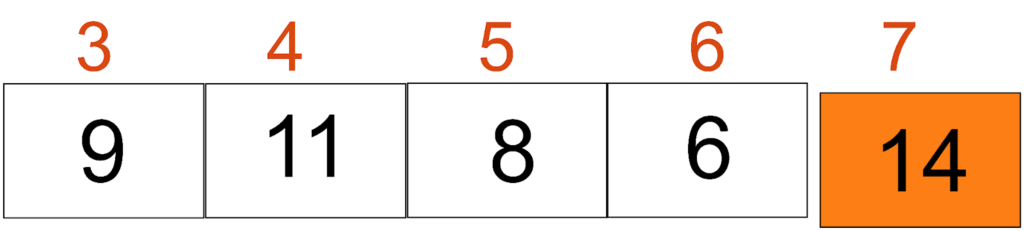
Here, the array will only be partitioned into one sub-array since there are no elements on the right side. Therefore, the resulting sub-array will have only elements [9, 11, 8, 6]. The pivot for this sub-array would be 9, as shown in the image below. 14 is at its correct position 7.
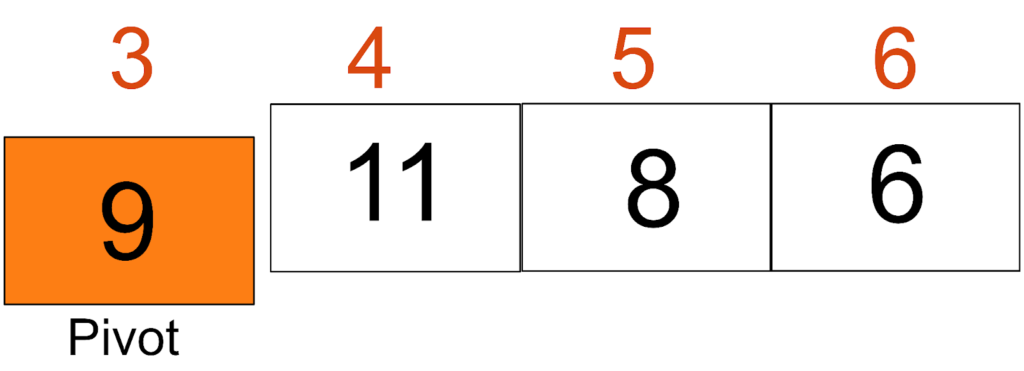
Now, the elements smaller than pivot (9) would move to the left side, and greater elements will move to the right side. So the pivot will move to position 5.
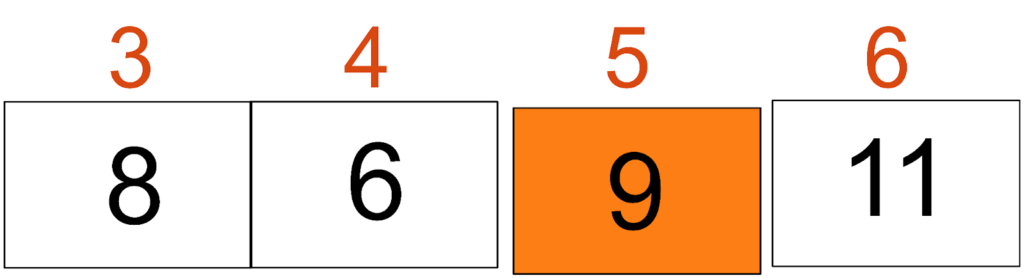
Now, the above array will be divided into two sub-arrays: one has elements [8, 6] and the other has only a single element, i.e. [11]. Therefore, we will not perform any operation with element 11 because it is single and cannot be further divided into sub-arrays. So, we have only one sub-array remaining, i.e. [8, 6]. 9 & 11 are at correct positions 5 and 6.
In this subarray, the pivot would be element 8, so we choose this element as a pivot and move it to its correct position, i.e. position 4, resulting in [6, 8]. If we further divide this array, it will be divided into sub-arrays with only one element, and we cannot perform any further operations on these single elements. Therefore, the divide algorithm ends here, meaning we can only divide the array up to this level. 6 and 8 also got their correct positions 3 and 4.
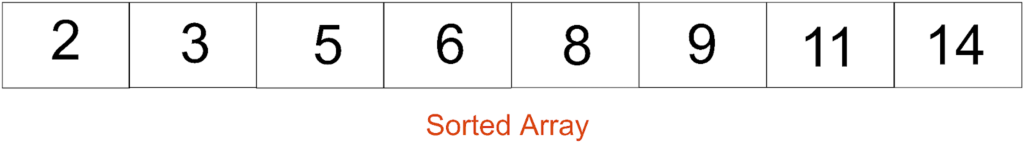
Finally, combine all the elements at their positions and you will get the final sorted array.
3. Implementation of Quicksort in Java
Now, let us have a look at the implementation of quicksort in Java.
- The quicksort() function checks whether the argument array has more than one element. If the subarray has only one element or is empty, then it is already sorted, and the function returns. Else, the partitioning is performed.
- The partitioning depends on the pivot element. The selection of pivot element is tricky, so to keep things simple, we can choose a fixed position element in the array. Such as, in our example, the pivot has been selected as the first element for every sub-array. We can optionally choose the last element of the array or any other random position.
- The function then recursively calls the quickSort function for the two subarrays created by the partition. This process continues until the entire subarray is sorted.
- Combine the sorted subarrays to get the final sorted array.
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Quicksort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {5, 9, 2, 11, 14, 6, 3, 8};
System.out.println("Unsorted array: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
quicksort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
System.out.println("Sorted array: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void quicksort(int[] arr, int start, int end) {
if(arr != null && arr.length <= 1) {
return;
}
if (start < end) {
int pivotIndex = partition(arr, start, end);
quicksort(arr, start, pivotIndex - 1);
quicksort(arr, pivotIndex + 1, end);
}
}
public static int partition(int[] arr, int start, int end) {
int pivot = arr[start];
int i = start;
for (int j = start + 1; j <= end; j++) {
if (arr[j] < pivot) {
i++;
swap(arr, i, j);
}
}
swap(arr, start, i);
return i;
}
public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}4. Performance
4.1. Time Complexity
An algorithm that uses the divide-and-conquer approach has a time complexity of O(n log n). Similarly, quicksort has an average time complexity of O(n log n).
However, if the input array is already sorted or nearly sorted and the pivot element is either the smallest or largest element in the array, the partition function will create a skewed partition. This means that one side of the partition will have no elements, while the other side will have the elements. In this case, the worst-case time complexity of quicksort becomes O(n2).
- Best case: O(n log n)
- Average case: O(n log n)
- Worst case: O(n2)
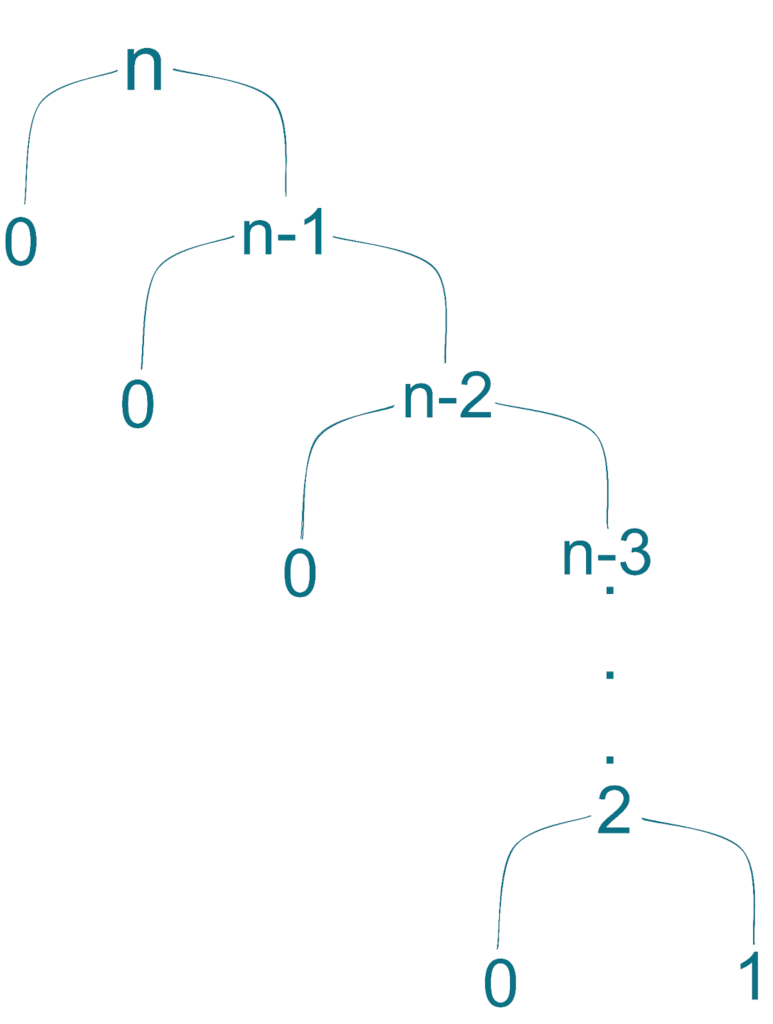
4.2. Space Complexity
Basic implementations of quicksort have a space complexity of O(log n) for recursive calls. However, in a worst-case scenario, where the partition function creates a skewed partition, the space complexity can reach O(n).
- Best case: O(log n)
- Average case: O(log n)
- Worst case: O(n)
5. Advantages and Disadvantages of Quicksort
5.1. Advantages
- In-place sorting: Quicksort sorts the input array in place without requiring any additional memory.
- Efficiency: Quicksort has an average-case time complexity of O(n log n), making it one of the fastest sorting algorithms.
- Ease of implementation: Quicksort is relatively easy to implement and can be customized to fit specific requirements.
5.2. Disadvantages
- Worst-case performance: As previously mentioned, quicksort can have a worst-case time complexity of O(n2) if the input array is already sorted or almost sorted.
- Unstable sorting: Quicksort is an unstable sorting algorithm, meaning it may not maintain the order of equal elements in the input array.
- Pivot element: Quicksort’s performance heavily relies on selecting the pivot element. If a lousy pivot element is chosen, it can result in a skewed partition and impact sorting performance.
6. Conclusion
In this article, we have gone through the visualization and implementation of quicksort, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of using this sorting algorithm. Furthermore, we have discussed how the choice of pivot element can impact sorting performance.
Happy Learning !!


Comments