Template method design pattern is widely accepted behavioral design pattern to enforce some sort of algorithm (fixed set of steps) in the context of programming.
It defines the sequential steps to execute a multi-step algorithm and optionally can provide a default implementation as well (based on requirements).
Table of Contents Introduction Problem Statement Solution Code Implementation Key Design Points Popular implementations of template method pattern Summary
Introduction
Have you faced any situation in your programming where you need to define a set of specific steps every time with a fixed order so that this can be enforced by implementation classes? If so, then template method pattern is the solution for you which can be used to enforce these steps (algorithm) in an orderly manner.
Applicability of template method pattern
- When we have pre-defined steps to achieve some algorithm.
- When we want to avoid duplicating code, moving the common implementation and steps in the base class.
Now let’s solve a design problem to understand it in detail.
Problem Statement
Lets say we need to build any house which is generally have certain steps. Some steps have default implementation and some steps are very specific to implementer with no default implementation.
Steps with default implementation
- Construction of base foundation
- Construction of roof
Steps with “NO” default implementation
- Construction of walls
- Construction of windows and doors
- Painting
- Interior decorating
We want to enforce these steps sequentially by all implementing classes in the application.
Solution
In above problem, we have certain steps in fixed order which all building classes must follow. So, we can use template method design pattern to solve this problem.
Let’s define a base class House which will have all the steps as methods and a template method buildhouse() which will call the intermediate steps – sequentially.
We also will create derived classes based on the type of the houses like GlassWallHouse and ConcreteWallHouse.
Class Diagram
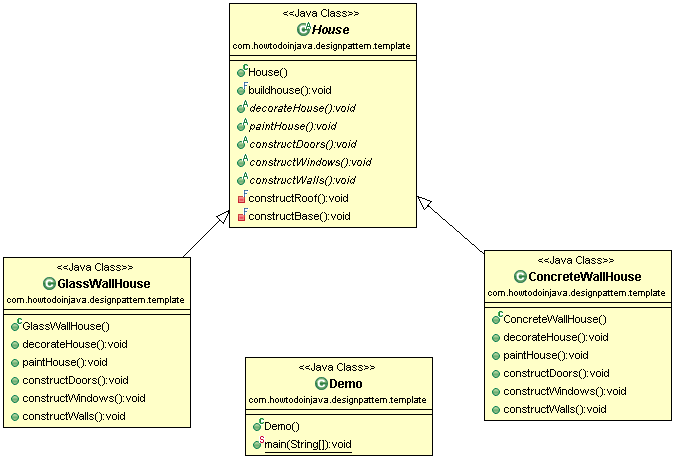
Code Implementation
First, we need to create a abstract class called House which will define the template method called buildHouse().
House.java
package com.howtodoinjava.designpattern.template;
/**
* abstract class House containing template method buildHouse and implementation
* of steps which is same for all types of houses. Those implementations have
* been marked as final.
*/
public abstract class House {
/**
* This is the template method we are discussing. This method should be
* final so that other class can't re-implement and change the order of the
* steps.
*/
public final void buildhouse() {
constructBase();
constructRoof();
constructWalls();
constructWindows();
constructDoors();
paintHouse();
decorateHouse();
}
public abstract void decorateHouse();
public abstract void paintHouse();
public abstract void constructDoors();
public abstract void constructWindows();
public abstract void constructWalls();
/**
* final implementation of constructing roof - final as all type of house
* Should build roof in same manner.
*/
private final void constructRoof() {
System.out.println("Roof has been constructed.");
}
/**
* final implementation of constructing base - final as all type of house
* Should build base/foundation in same manner.
*/
private final void constructBase() {
System.out.println("Base has been constructed.");
}
}
Now we are going to create two implementations of this class which can be used to build concrete houses and glass houses.
ConcreteWallHouse.java
package com.howtodoinjava.designpattern.template;
public class ConcreteWallHouse extends House {
@Override
public void decorateHouse() {
System.out.println(“Decorating Concrete Wall House”);
}
@Override
public void paintHouse() {
System.out.println(“Painting Concrete Wall House”);
}
@Override
public void constructDoors() {
System.out.println(“Constructing Doors for Concrete Wall House”);
}
@Override
public void constructWindows() {
System.out.println(“Constructing Windows for Concrete Wall House”);
}
@Override
public void constructWalls() {
System.out.println(“Constructing Concrete Wall for my House”);
}
}
GlassWallHouse.java
package com.howtodoinjava.designpattern.template;
public class GlassWallHouse extends House {
@Override
public void decorateHouse() {
System.out.println("Decorating Glass Wall House");
}
@Override
public void paintHouse() {
System.out.println("Painting Glass Wall House");
}
@Override
public void constructDoors() {
System.out.println("Constructing Doors for Glass Wall House");
}
@Override
public void constructWindows() {
System.out.println("Constructing Windows for Glass Wall House");
}
@Override
public void constructWalls() {
System.out.println("Constructing Glass Wall for my House");
}
}
Demo
Let’s try to build houses of both types.
package com.howtodoinjava.designpattern.template;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(“Going to build Concrete Wall House”);
House house = new ConcreteWallHouse();
house.buildhouse();
System.out.println(“Concrete Wall House constructed successfully”);
System.out.println(“********************”);
System.out.println(“Going to build Glass Wall House”);
house = new GlassWallHouse();
house.buildhouse();
System.out.println(“Glass Wall House constructed successfully”);
}
}
Output:
Going to build Concrete Wall House Base has been constructed. Roof has been constructed. Constructing Concrete Wall for my House Constructing Windows for Concrete Wall House Constructing Doors for Concrete Wall House Painting Concrete Wall House Decorating Concrete Wall House Concrete Wall House constructed successfully ******************** Going to build Glass Wall House Base has been constructed. Roof has been constructed. Constructing Glass Wall for my House Constructing Windows for Glass Wall House Constructing Doors for Glass Wall House Painting Glass Wall House Decorating Glass Wall House Glass Wall House constructed successfully
Key Design Points
- Mark template method as final so that implementing class can’t override and change the order of steps.
- In base class, implement all the methods with default implementation so the derived classes need not to define them.
- Mark all methods abstract which derived classes must implement.
Popular implementations of template method pattern
These are few popular existing implementations of template method design pattern.
- Non-abstract methods of
InputStream,OutputStream,Reader,Writerfrom Java IO. - Non-abstract methods of some abstract collection classes like
AbstractList,AbstractSet,AbstractMapetc.
Summary
Template pattern is a very easy design pattern which is used to define and enforcing certain sequential algorithm steps in programming paradigm. It helps in defining the skeleton of an algorithm, which shall not be overridden in sub classes.
So going forward, when you need to implement above mentioned business scenarios, think of template pattern – it is very much easy to implement as well as it is very much maintainable also.
Happy Learning !!

Comments