JSR-303 bean validation is an specification whose objective is to standardize the validation of Java beans through annotations. The objective of the JSR-303 standard is to use annotations directly in a Java bean class.
JSR 303 specification allows the validation rules to be specified directly into the fields inside any Java class which they are intended to validate, instead of creating validation rules in separate classes.
So far, we have learned about bean validations in Spring MVC using BindingResult.rejectValue() and custom validator implementation. In this example we will learn about validating spring managed beans using JSR-303 annotations.
Read More : Spring MVC Submit Form Example & Spring MVC Custom Validator Example
After applying the validation in this post, the error messages on the UI will look like this:
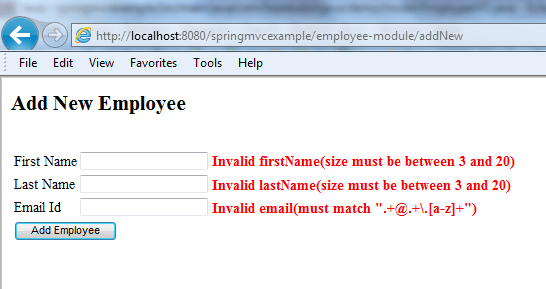
1. Adding JSR-303 and Hibernate Validator Dependency
To use JSR-303 annotations with Spring, you will need to add below dependency in pom.xml.
<dependency> <groupId>javax.validation</groupId> <artifactId>validation-api</artifactId> <version>1.0.0.GA</version> </dependency>
For validation to actually work, you need an implementation as well, such as Hibernate Validator.
<dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId> <version>4.3.1.Final</version> </dependency>
2. Applying JSR-303 Annotations
After adding JSR-303 dependencies, the first thing you need to do is decorate a Java bean with the necessary JSR-303 annotations. See below EmployeeVO class whose fields are annotated with annotations such as @Size and @Pattern.
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.validation.constraints.Pattern;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
public class EmployeeVO implements Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Integer id;
@Size(min = 3, max = 20)
private String firstName;
@Size(min = 3, max = 20)
private String lastName;
@Pattern(regexp=".+@.+\\.[a-z]+")
private String email;
//Setters and Getters
@Override
public String toString() {
return "EmployeeVO [id=" + id + ", firstName=" + firstName
+ ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email=" + email + "]";
}
}
Read More : List of all supported JSR-303 annotations
3. Controller changes
To apply bean validation, we need to perform the following modification to the controller.
1. Include validator reference to controller class so that we can access it across all methods in controller.
private Validator validator;
2. Next change is in controller’s post method which is called when user submit the form.
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String submitForm(@ModelAttribute("employee") EmployeeVO employeeVO,
BindingResult result, SessionStatus status) {
Set<ConstraintViolation<EmployeeVO>> violations = validator.validate(employeeVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<EmployeeVO> violation : violations)
{
String propertyPath = violation.getPropertyPath().toString();
String message = violation.getMessage();
// Add JSR-303 errors to BindingResult
// This allows Spring to display them in view via a FieldError
result.addError(new FieldError("employee",propertyPath,
"Invalid "+ propertyPath + "(" + message + ")"));
}
if (result.hasErrors()) {
return "addEmployee";
}
// Store the employee information in database
// manager.createNewRecord(employeeVO);
// Mark Session Complete
status.setComplete();
return "redirect:addNew/success";
}
Please note that unlike the earlier Spring specific validation approaches, the validator field is not assigned to any bean, but rather a factory class of the type javax.validation.ValidatorFactory. This is how JSR-303 validation works. The assignment process is done inside the controller’s constructor.
In submitForm() method, the first step consists of creating a Set of the type javax.validation.ConstraintViolation to hold any errors detected from validating the instance of the EmployeeVO object. The value assigned to this Set results from executing validator.validate(employeeVO), which is used to run the validation process on the employeeVO field that is an instance of the EmployeeVO object.
Once the validation process is complete, a loop is declared over the violations Set to extract any possible validation errors encountered in the EmployeeVO object. Since the violations Set contains JSR-303 specific errors, it’s necessary to extract the raw error messages and place them in a Spring MVC specific format. This allows validation errors to be displayed in a view managed by Spring as if they are generated by a Spring validator.
4. Demo
That’s all. JSR-303 validation configuration is complete. Now test the application.
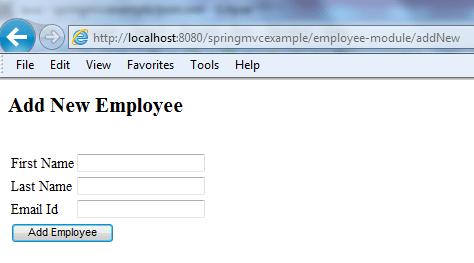
1. Enter URL: http://localhost:8080/springmvcexample/employee-module/addNew
It will display a blank form.
2. Without filling any field, submit the form. You will get error specific to each field.

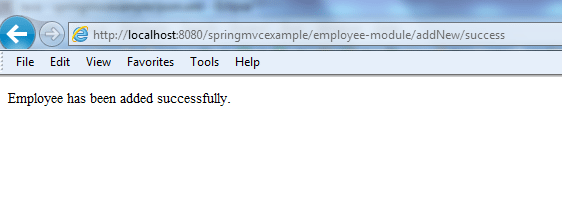
3. Fill all fields and press Submit button. Success page will be displayed.
5. Complete Code
For reference, complete pom.xml file is below:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 ; <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.howtodoinjava.demo</groupId> <artifactId>springmvcexample</artifactId> <packaging>war</packaging> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>springmvcexample Maven Webapp</name> <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- Spring MVC support --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>4.1.4.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>4.1.4.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- Tag libs support for view layer --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>taglibs</groupId> <artifactId>standard</artifactId> <version>1.1.2</version> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <!-- JSR 303 Dependencies --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.validation</groupId> <artifactId>validation-api</artifactId> <version>1.0.0.GA</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId> <version>4.3.1.Final</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>springmvcexample</finalName> </build> </project>
And EmployeeController class is as below:
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.controller;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolation;
import javax.validation.Validation;
import javax.validation.Validator;
import javax.validation.ValidatorFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.SessionAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.bind.support.SessionStatus;
import com.howtodoinjava.demo.model.EmployeeVO;
import com.howtodoinjava.demo.service.EmployeeManager;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/employee-module/addNew")
@SessionAttributes("employee")
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
EmployeeManager manager;
private Validator validator;
public EmployeeController()
{
ValidatorFactory validatorFactory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
validator = validatorFactory.getValidator();
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String setupForm(Model model) {
EmployeeVO employeeVO = new EmployeeVO();
model.addAttribute("employee", employeeVO);
return "addEmployee";
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String submitForm(@ModelAttribute("employee") EmployeeVO employeeVO,
BindingResult result, SessionStatus status) {
Set<ConstraintViolation<EmployeeVO>> violations = validator.validate(employeeVO);
for (ConstraintViolation<EmployeeVO> violation : violations)
{
String propertyPath = violation.getPropertyPath().toString();
String message = violation.getMessage();
// Add JSR-303 errors to BindingResult
// This allows Spring to display them in view via a FieldError
result.addError(new FieldError("employee",propertyPath,
"Invalid "+ propertyPath + "(" + message + ")"));
}
if (result.hasErrors()) {
return "addEmployee";
}
// Store the employee information in database
// manager.createNewRecord(employeeVO);
// Mark Session Complete
status.setComplete();
return "redirect:addNew/success";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/success", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String success(Model model) {
return "addSuccess";
}
}
6. JSR 303 Annotations List
| Constraint | Description |
|---|---|
| @AssertFalse | The field value must be false. |
| @AssertTrue | The field value must be true. |
| @DecimalMax | The field value must be a decimal value lower than or equal to the number in the value element. |
| @DecimalMin | The field value must be a decimal value greater than or equal to the number in the value element. |
| @Digits | The field value must be a number within a specified range. |
| @Future | The field value must be a Date in the future. |
| @Max | The field value must be an integer value lower than or equal to the number in the value element. |
| @Min | The field value must be an integer value greater than or equal to the number in the value element. |
| @NotNull | The field value must not be null. |
| @Null | The field value must be null. |
| @Past | The field value must be a Date in the past. |
| @Pattern | The field value must match the regular expression defined in the regex element. |
| @Size | The field size is evaluated and must match the specified min and max boundaries. |
Drop me your queries in the comments section.
Happy Learning !!


Comments