TestNG lifecycle is controlled via lifecycle annotations. These lifecycle annotations are mainly the before and after annotations that are used to execute a certain set of code before and after the execution of actual tests.
These lifecycle methods are used to basically set up test infrastructure before the start of test execution and then to cleanup any of these things after the test execution ends.
1. TestNG Before and After Annotations
TestNG provides five different kinds of Before and After annotation options, each of which can be used depending upon the test requirements.
The following are different before and after lifecycle annotations provided by TestNG.
| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
| @BeforeSuite | The annotated method will be run before all tests in this suite have run. |
| @BeforeTest | The annotated method will be run before any test method belonging to the classes inside the test tag is run. |
| @BeforeGroups | The list of groups that this configuration method will run before. This method is guaranteed to run shortly before the first test method that belongs to any of these groups is invoked. |
| @BeforeClass | The annotated method will be run before the first test method in the current class is invoked. |
| @BeforeMethod | The annotated method will be run before all the test methods in the current class have been run. |
| @AfterSuite | The annotated method will be run after all tests in this suite have run. |
| @AfterTest | The annotated method will be run after all the test methods belonging to the classes inside the test tag have run. |
| @AfterGroups | The list of groups that this configuration method will run after. This method is guaranteed to run shortly after the last test method that belongs to any of these groups is invoked. |
| @AfterClass | The annotated method will be run after all the test methods in the current class have been run. |
| @AfterMethod | The annotated method will be run after each test method. |
By default, all given above annotations run in the sequence discussed in the next section. Though, we can control the execution of these annotations using the attributes under specific requirements.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| alwaysRun | If set to true, this configuration method will be run regardless of what groups it belongs to, or even if one or more methods invoked previously failed or was skipped. |
| dependsOnGroups | The list of groups this method depends on. |
| dependsOnMethods | The list of methods this method depends on. |
| enabled | Enabled if set to true. Default is true. |
| groups | The list of groups this method belongs to. |
| inheritGroups | If true, this method will belong to groups specified in the @Test annotation at the class level. |
| onlyForGroups | Only for @BeforeMethod and @AfterMethod. |
2. Lifecycle Sequence
Following is the sequence in which the lifecycle annotated methods will get executed.
- @BeforeSuite
- @BeforeTest
- @BeforeClass
- @BeforeMethod
- @Test
- @AfterMethod
- @AfterClass
- @AfterTest
- @AfterSuite
3. Test Lifecycle Demo
Let’s try out an example containing all the preceding annotated methods and learn about when they are executed.
Create a new TestNG test having all before and after annotations. You can create this test with help of instructions given in this TestNG tutorial. Let’s see how you can select all before and after annotations.
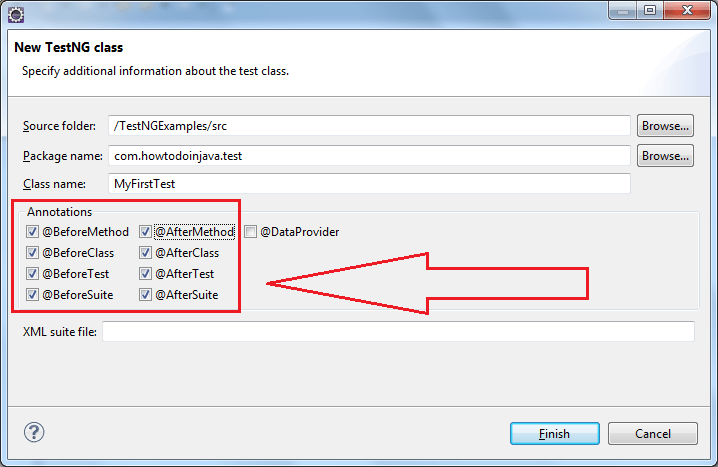
After clicking on OK, you will get a test with all annotations. Add some print statements in all methods so that they can be tracked in which order they are executed.
import org.testng.annotations.AfterClass;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterSuite;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterTest;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeSuite;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeTest;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class MyFirstTest
{
@Test
public void testCase() {
}
@BeforeSuite
public void beforeSuite() {
System.out.println("Before Suite method");
}
@AfterSuite
public void afterSuite() {
System.out.println("After Suite method");
}
@BeforeTest
public void beforeTest() {
System.out.println("Before Test method");
}
@AfterTest
public void afterTest() {
System.out.println("After Test method");
}
@BeforeClass
public void beforeClass() {
System.out.println("Before Class method");
}
@AfterClass
public void afterClass() {
System.out.println("After Class method");
}
@BeforeMethod
public void beforeMethod() {
System.out.println("Before Method");
}
@AfterMethod
public void afterMethod() {
System.out.println("After Method");
}
}Now run the above test as the TestNG test and you will get the following output in the console.
[TestNG] Running:
C:\Users\somepath\testng-customsuite.xml
Before Suite method
Before Test method
Before Class method
Before Method
After Method
After Class method
After Test method
PASSED: testCase
===============================================
Default test
Tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
After Suite method
===============================================
Default suite
Total tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
[TestNG] Time taken by org.testng.reporters.XMLReporter@177b3cd: 19 ms
[TestNG] Time taken by [FailedReporter passed=0 failed=0 skipped=0]: 0 ms
[TestNG] Time taken by org.testng.reporters.jq.Main@b8deef: 53 ms
[TestNG] Time taken by org.testng.reporters.JUnitReportReporter@10ab323: 13 ms
[TestNG] Time taken by org.testng.reporters.EmailableReporter2@5e176f: 11 ms
[TestNG] Time taken by org.testng.reporters.SuiteHTMLReporter@d1e89e: 184 msCongratulations, you have successfully created a test class with all kinds of before and after annotations and executed it.
4. Lifecycle Methods in Parent and Child Classes
The above example only contains annotations that are present in the same class. Let’s learn the execution flow when a class containing annotations is extended by another class having another set of before and after annotations.
TestNG guarantees that the “@Before” methods are executed in inheritance order (highest superclass first, then going down the inheritance chain), and the “@After” methods in reverse order (going up the inheritance chain).
Let’s create two new classes BaseClass and ChildClass. Then add similar before/after annotations on both of them. Here the main thing to notice is that ChildClass extends BaseClass. And Test is defined in ChildClass class.
4.1. BaseClass.java
import org.testng.annotations.AfterClass;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeMethod;
public class BaseClass {
@BeforeMethod
public void beforeMethod() {
System.out.println("BaseClass's Before Test method");
}
@AfterMethod
public void afterMethod() {
System.out.println("BaseClass's After Test method");
}
@BeforeClass
public void beforeClass() {
System.out.println("BaseClass's Before Class method");
}
@AfterClass
public void afterClass() {
System.out.println("BaseClass's After Class method");
}
}4.2. ChildClass.java
import org.testng.annotations.AfterClass;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class ChildClass extends BaseClass {
@BeforeMethod
public void beforeChildMethod() {
System.out.println("ChildClass's Before Test method");
}
@AfterMethod
public void afterChildMethod() {
System.out.println("ChildClass's After Test method");
}
@BeforeClass
public void beforeChildClass() {
System.out.println("ChildClass's Before Class method");
}
@AfterClass
public void afterChildClass() {
System.out.println("ChildClass's After Class method");
}
@Test
public void testCase() {
System.out.println("===== Executing actual test ======");
}
}4.3. Execution Sequence of Lifecycle Methods
Executing ChildClass test will generate the below output.
[TestNG] Running:
C:\Users\somepath\testng-customsuite.xml
BaseClass's Before Class method
ChildClass's Before Class method
BaseClass's Before Test method
ChildClass's Before Test method
===== Executing actual test ======
ChildClass's After Test method
BaseClass's After Test method
ChildClass's After Class method
BaseClass's After Class method
PASSED: testCase
===============================================
Default test
Tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
===============================================
Default suite
Total tests run: 1, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================
[TestNG] Time taken by org.testng.reporters.EmailableReporter2@1549f94: 13 ms
[TestNG] Time taken by [FailedReporter passed=0 failed=0 skipped=0]: 0 ms
[TestNG] Time taken by org.testng.reporters.XMLReporter@1bd7848: 16 ms
[TestNG] Time taken by org.testng.reporters.jq.Main@1342ba4: 52 ms
[TestNG] Time taken by org.testng.reporters.JUnitReportReporter@176e552: 12 ms
[TestNG] Time taken by org.testng.reporters.SuiteHTMLReporter@ff057f: 190 msAs you can see from the report output:
- TestNG first executes the @Before annotated methods from the parent class and then from the child class.
- Then the test execution happens.
- The @After annotated methods are executed first in the child class and then in the parent class.
Happy Learning !!


Comments