The ability to group the related tests is one of the most important features of TestNG. Users can group multiple tests into a named group. The user can execute a particular set of tests belonging to a group or multiple groups.
- The test grouping feature allows the tests to be segregated into different sections or modules. For example, we can have a set of tests that belong to the sanity tests whereas others may belong to regression tests.
- We can also segregate the tests based on the functionalities/features that the test verifies. This helps in executing only a particular set of tests as and when required.
1. Creating Test Groups
Let’s create a test class, which contains certain tests that belong to a group name test-group. To do this, use groups attribute of @Test annotation.
package com.howtodoinjava.groupExamples;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class TestGroupExample
{
@Test(groups = { "test-group" })
public void testMethodOne() {
System.out.println("Test method one belonging to group.");
}
@Test
public void testMethodTwo() {
System.out.println("Test method two not belonging to group.");
}
@Test(groups = { "test-group" })
public void testMethodThree() {
System.out.println("Test method three belonging to group.");
}
}If we will run the above tests, then test execution does not consider any grouping and hence executes all the tests in the specified test class.
If we want to execute methods under a certain group only, then you can execute them in the given ways discussed in the following two sections.
2. Execute Test Groups in IDE
In the earlier section, we created a test class with certain tests that belonged to a test group. Now let’s run the group of tests using eclipse.
- Go to Run | Run Configurations.
- Select TestNG from the list of available configurations and click on the new configuration icon.
- In the new configuration window give a configuration name, for example, TestGroupExample.
- Go to the Project section and click on the Browse button. Select the previously created project that is TestNGExamples.
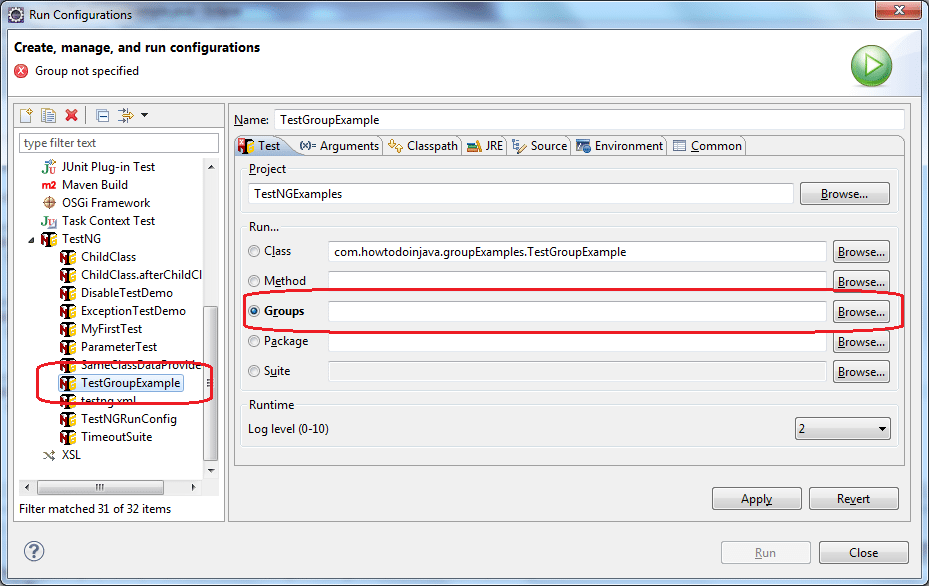
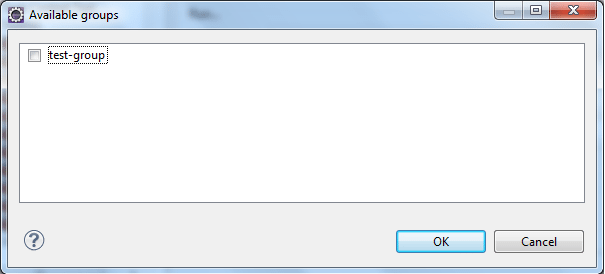
- Go to the Groups section and click on the Browse button. Select the group which you would like to execute from the list, in this case it’s test-group.
- Click on the
Applybutton and then click onRun.
The following results will be shown in the TestNG’s Results window of Eclipse:
Test method one belonging to group.
Test method three belonging to group.
PASSED: testMethodOne
PASSED: testMethodThree
===============================================
GRP-test-group
Tests run: 2, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================Congratulations, we have successfully executed test methods that belonged to a particular group using the TestNG runner configuration in Eclipse.
We can also use this technique to execute multiple groups by selecting the respective groups in the Browse section. Normally it’s better to use the TestNG-XML-based execution to execute test methods that belong to a particular group.
See Also: Setting Up TestNG in Eclipse
3. Execute Test Groups with testng.xml
Now let’s learn how to create a TestNG XML file to execute tests that belong to a particular group. This method is the preferred and easy way to execute groups. Also, these TestNG XML files can then be used with the build tools to execute TestNG test suites.
Open Eclipse and create a new file with the name testng.xml in the previously created project.
Add the following code to the said file:
<suite name="Time test Suite" verbose="1">
<test name="Group Test">
<groups>
<run>
<include name="test-group" />
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="com.howtodoinjava.groupExamples.TestGroupExample" />
</classes>
</test>
</suite> The above XML file contains only one test inside a suite. This contains the groups section as shown in the code. The run tag represents the group that needs to be run. The include tag represents the name of the group that needs to be executed.
Select the previously created testng XML file and run it as a TestNG suite. You will see the following test results:
Test method one belonging to group.
Test method three belonging to group.
===============================================
Time test Suite Total tests run: 2, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================Great. We successfully created a testng XML file that creates a test in the said suite by including a group in it.
The user can also provide the package names for the tests. TestNG will search all the classes that are added to the test to include or exclude particular test methods that belong to particular groups. Once found, these test methods will then be executed by TestNG as a test suite.
4. Writing Tests Belonging to Multiple Groups
Earlier we learned about creating tests that belonged to a single group, but TestNG allows test methods to belong to multiple groups also. This can be done by providing the group names as an array in the groups attribute of the @Test annotation.
Let’s create a sample program with multiple groups to learn how it is done.
package com.howtodoinjava.groupExamples;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class MultiGroupExample
{
@Test(groups = { "group-one" })
public void testMethodOne() {
System.out.println("Test method one belonging to group.");
}
@Test(groups = { "group-one", "group-two" })
public void testMethodTwo() {
System.out.println("Test method two belonging to both group.");
}
@Test(groups = { "group-two" })
public void testMethodThree() {
System.out.println("Test method three belonging to group.");
}
}The preceding class contains three test methods. Two of the test methods belong to one group each, whereas one of the methods belongs to two groups, group-one, and group-two respectively.
Now edit the testng.xml file like below:
<suite name="Multi Group Suite" verbose="1">
<test name="Group Test one">
<groups>
<run>
<include name="group-one" />
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="com.howtodoinjava.groupExamples.MultiGroupExample" />
</classes>
</test>
<test name="Group Test two">
<groups>
<run>
<include name="group-two" />
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="com.howtodoinjava.groupExamples.MultiGroupExample" />
</classes>
</test>
</suite>The preceding TestNG XML suite contains two tests, each of them executing test methods belonging to a particular group. Select TestNG XML file and run it as a TestNG suite. You will see the following test results:
Test method one belonging to group.
Test method two belonging to both group.
Test method three belonging to group.
Test method two belonging to both group.
===============================================
Multi Group Suite
Total tests run: 4, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================Here we have successfully created a test method, which belongs to multiple groups and can be executed successfully. As you can see in the previous test result, testMethodTwo() was executed in both the tests of the test suite. This is because it belongs to both of the groups whose test methods are executed by TestNG.
5. Including and Excluding Groups from Test Suite
TestNG also allows you to include and exclude certain groups from test execution. This helps in executing only a particular set of tests and excluding certain tests.
A simple example can be when a feature is broken and you need to exclude a fixed set of tests from execution since these tests will fail upon execution. Once the feature is fixed you can then verify the feature by just executing the respective group of tests.
Let’s create a sample program and learn how to exclude a group of tests.
package com.howtodoinjava.groupExamples;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class ExcludeGroupTest
{
@Test(groups = { "include-group" })
public void testMethodOne() {
System.out.println("Test method one belonging to include group.");
}
@Test(groups = { "include-group" })
public void testMethodTwo() {
System.out.println("Test method two belonging to include group.");
}
@Test(groups = { "include-group", "exclude-group" })
public void testMethodThree() {
System.out.println("Test method three belonging to exclude/include groups.");
}
}The preceding class contains three test methods that print a message onto the console when executed.
All three methods belong to a group include-group whereas the testMethodThree() method also belongs to the group exclude-group.
<suite name="Exclude Group Suite" verbose="1">
<test name="Exclude Group Test">
<groups>
<run>
<include name="include-group" />
<exclude name="exclude-group" />
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="com.howtodoinjava.groupExamples.ExcludeGroupTest" />
</classes>
</test>
</suite>Now run above testng.xml file and it will produce the below result.
Test method one belonging to include group.
Test method two belonging to include group.
===============================================
Exclude Group Suite
Total tests run: 2, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================As you can see from the previous test results TestNG executed two methods from the group include-group and excluded the third method that belonged to the group exclude-group, which was excluded from the test execution.
Note
If a test method belongs to both included and excluded groups, the excluded group takes priority and the test method will be excluded from the test execution.
6. Group Names Containing Regular Expressions
While configuring the tests by including or excluding groups, TestNG allows the user to use regular expressions. This helps users to include and exclude groups based on a name search.
Let’s learn how to exclude tests based on regex-based name matching.
package com.howtodoinjava.groupExamples;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class RegularExpressionGroupTest
{
@Test(groups = { "include-test-one" })
public void testMethodOne() {
System.out.println("Test method one");
}
@Test(groups = { "include-test-two" })
public void testMethodTwo() {
System.out.println("Test method two");
}
@Test(groups = { "test-one-exclude" })
public void testMethodThree() {
System.out.println("Test method three");
}
@Test(groups = { "test-two-exclude" })
public void testMethodFour() {
System.out.println("Test method Four");
}
}And testng.xml file.
<suite name="Regular Exp. Group Suite" verbose="1"&>
<test name="Regular Exp. Test"&>
<groups&>
<run&>
<include name="include.*" /&>
<exclude name=".*exclude" /&>
</run&>
</groups&>
<classes&>
<class name="com.howtodoinjava.groupExamples.RegularExpressionGroupTest" /&>
</classes&>
</test&>
</suite&>The preceding XML contains a simple test in which all the groups with a name starting with include are included, whereas all the groups with the name ending with excluding are excluded from your test execution.
Now run the testng.xml file and you will get the below result in the console.
Test method one
Test method two
===============================================
Regular Exp. Group Suite
Total tests run: 2, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================Here TestNG executed two methods that belong to groups with a name starting with include and excluded the test methods that belonged to groups with names ending with exclude.
Note
To use regular expressions to include and exclude groups you have to use .* for matching names.
We can also use it for searching groups that contain a certain string in their names by using the expression at the start and end of the search string (for example, .name.).
6. Default Groups
Sometimes we may need to assign a default group to a set of test methods that belong to a class. This way all the public methods that belong to the said class will automatically become tests and become part of the said group.
This can be achieved by using the @Test annotation at class level and defining the default group in the said @Test annotation.
@Test(groups={"default-group"})
public class DefaultGroup {
public void testMethodOne(){
System.out.println("Test method one.");
}
public void testMethodTwo(){
System.out.println("Test method two.");
}
@Test(groups={"test-group"})
public void testMethodThree(){
System.out.println("Test method three.");
}
}7. Group of Groups or ‘Meta Groups’
TestNG allows users to create groups out of existing groups and then use them during the creation of the test suite. You can create new groups by including and excluding certain groups and then use them.
Let’s create a sample test program and learn how to create a group of groups called MetaGroups.
package com.howtodoinjava.groupExamples;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class RegularExpressionGroupTest
{
@Test(groups = { "include-test-one" })
public void testMethodOne() {
System.out.println("Test method one");
}
@Test(groups = { "include-test-two" })
public void testMethodTwo() {
System.out.println("Test method two");
}
@Test(groups = { "test-one-exclude" })
public void testMethodThree() {
System.out.println("Test method three");
}
@Test(groups = { "test-two-exclude" })
public void testMethodFour() {
System.out.println("Test method Four");
}
}Now create testng.xml file like below:
<suite name="Group of group Suite" verbose="1"&>
<test name="Group of group Test"&>
<groups&>
<define name="include-group"&>
<include name="include-test-one" /&>
<include name="include-test-two" /&>
</define&>
<define name="exclude-group"&>
<include name="test-one-exclude" /&>
<include name="test-two-exclude" /&>
</define&>
<run&>
<include name="include-group" /&>
<exclude name="exclude-group" /&>
</run&>
</groups&>
<classes&>
<class name="com.howtodoinjava.groupExamples.RegularExpressionGroupTest" /&>
</classes&>
</test&>
</suite&>Here two groups of groups have been defined inside the test, and then these groups are used for test execution. The MetaGroup is created using the <define> tag inside the groups tag.
The name of the new group is defined using the name attribute under the define tag. Groups are included and excluded from the new group by using the include and exclude tags.
Now run the testng.xml test and it will produce the below result in the console:
Test method one
Test method two
===============================================
Group of group Suite
Total tests run: 2, Failures: 0, Skips: 0
===============================================Here, testNG executed only two methods, as mentioned in the included-group group and excluded the test methods that belong to the excluded-group. You can define as many groups of groups as you want.
That’s all related to testing groups in TestNG. Let me know if you have any queries.
Happy Learning !!




Comments