The Java ArrayList represents a resizable array of objects which allows us to add, remove, find, sort and replace elements. The ArrayList is part of the Collection framework and implements in the List interface.
1. Introduction to Java ArrayList
1.1. What is an ArrayList?
An ArrayList exhibits the following features:
- Ordered – Elements in ArrayList preserve their ordering which is by default the order in which these were added to the list.
- Index-based – Elements can be randomly accessed using index positions. Index starts with ‘0’.
- Dynamic resizing – ArrayList grows dynamically when more elements need to be added than its current size.
- Non-synchronized – ArrayList is not synchronized by default. The programmer needs to use the synchronized keyword appropriately or simply use the Vector class.
- Allows duplicate items – We can add duplicate elements in ArrayList. It is not possible in sets.
The java.util.ArrayList class extends AbstractList which implements List interface. The List extends Collection and Iterable interfaces in hierarchical order.
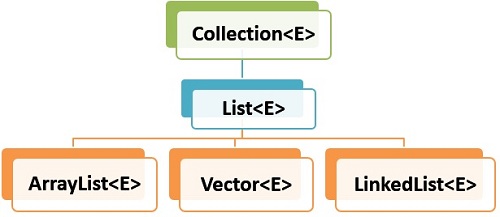
1.2. Internal Implementation
Internally, the ArrayList class is implemented using an array (also called a backing array). The elements that are added or removed from ArrayList are actually modified in the backing array. All ArrayList methods access this backing array and get/set elements in it.
public class ArrayList<E> ... {
transient Object[] elementData; //backing array
private int size; //array or list size
//...
}When we create an empty ArrayList, the array is initiated with default capacity 10. We keep adding items to the arraylist, and they are stored in the backing array.
When the array becomes full, and we add a new item, the resizing operation happens. In resizing, the size of the array is increased, such that it should never overflow the JVM limit. The items are copied from the previous array into this new array. The previous backing array is then free for garbage collection.
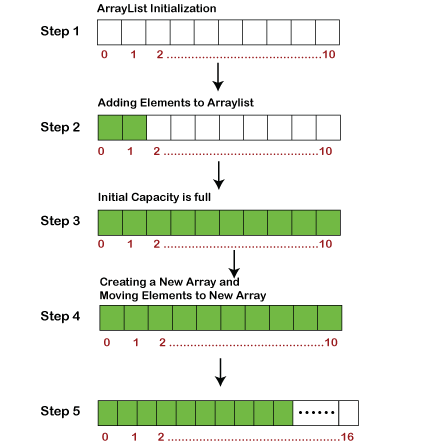
1.3. When to use ArrayList?
As mentioned earlier, ArrayList is a resizable-array implementation. When dealing with arrays, one of the major concerns is to always check for valid indices, else the program throws IndexOutOfBoundsException. The ArrayList never throws IndexOutOfBoundsException, and we can freely add/remove elements and ArrayList automatically handle resizing when elements are added or removed.
ArrayList is a part of the Java Collections Framework thus arraylist can be used with other collection types and Stream API in a seamless manner, providing a lot of flexibility in data handling.
When used with generics, ArrayList provides type safety at compile time and ensures that it will contain items only of a certain type, thus reducing the chances of ClassCastException in runtime.
2. Creating an ArrayList
We can create an arraylist in different ways under different scenarios. Let us check them out:
2.1. Using Constructors
The most straightforward way to create an ArrayList is by using its constructors. Its default no-argument constructor creates an empty ArrayList with the default initial capacity is 10.
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();Optionally, we can specify the initialCapacity into the constructor to avoid frequent resizing operations if we already know how many items we are going to store in it.
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(128);It is also possible to initialize an arraylist with the items from another list or collection by passing the collection to the constructor.
Set<String> set = ...;
//Initializes the list with items from the Set
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(set);2.2. Using Factory Methods
Since Java 9, we can use factory methods to initialize an ArrayList with items. For example, List.of() is a method that creates an immutable List with specified items. It is often used to create and initialize a List in one line. We can use it with ArrayList constructor to create an ArrayList and populate it with items in a single line.
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(List.of("a", "b", "c"));In the same way, we can use the Arrays.asList() factory method as well:
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c"));2.3. Creating ArrayList of Custom Objects
Although it seems pretty simple to store custom objects in ArrayList, still we must ensure that the custom object implements the equals() method properly and satisfies the requirements.
Consider the following Item class with two fields id and name. It does not define the equals method.
class Item {
long id;
String name;
public Item(long id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}When we add a few items to the list, and later try to check an item, we do not get the desired result. The item is not found.
ArrayList<Item> listOfItems = new ArrayList<>(List.of(new Item(1, "Item1"), new Item(2, "Item2")));
System.out.println( listOfItems.contains(new Item(1, "Item1")) ); //prints 'false'In our example, the assumption is that if two items have the same id then they must be equal. Let us write a custom equals() method:
class Item {
//...
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Item item = (Item) o;
return id == item.id;
}
}Now when we again run the example code, we get the correct result and the item is found in the list.
System.out.println( listOfItems.contains(new Item(1, "Item1")) ); //prints 'true'3. Common Operations
Now we have a basic understanding of ArrayList class, let us see its methods to be used in common CRUD operations:
3.1. Adding Items to an ArrayList
We can append items to an existing ArrayList using two methods:
add(e): appends the specified element to the end of the list and returns true, else false.addAll(): appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of the list, in the order that they are returned by the specified collection’s Iterator.
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add("a"); // [a]
arrayList.addAll(List.of("b", "c", "d")); // [a, b, c, d]To add an element at the specified position, we can use the add(index, element) method.
- It inserts the specified element at the specified position in the list.
- It also shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(List.of("a", "b", "c", "d"));
arrayList.add(2, "temp"); //[a, b, temp, c, d]3.2. Replacing elements in ArrayList
To replace an existing element with a new element, we can use the set(index, element) method.
ArrayList<String> listWithItems = new ArrayList<>(List.of("a", "b", "c", "d"));
System.out.println(listWithItems); //[a, b, c, d]
listWithItems.set(2, "T");
System.out.println(listWithItems); //[a, b, T, d]3.3. Removing elements from an ArrayList
ArrayList class provides two methods for removing the items:
remove(e): removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, if it is present, and returns true. Else, returns false.removeAll(collection): removes all of the elements that are contained in the specified collection. It returns true even if a single element is removed as the result of this operation, else returns false if the list is unchanged.
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(List.of("a", "b", "c", "d"));
list.remove("c"); // [a, b, d]
list.removeAll(List.of("b", "d")); // [a]We can use the clear() method to remove all the elements from the list in a single method call. It will make the list empty, with zero elements in it.
list.clear(); // []3.4. Checking ArrayList size
The get the size of the arraylist, or count the number of elements in the list, we can use the size() method.
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(List.of("a", "b", "c", "d"));
int size = list.size(); // 43.5. Checking if an ArrayList is empty
The isEmpty() method returns true if the list contains no elements. Else, returns false.
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
boolean isEmpty = list.isEmpty(); // true
list.add("a");
isEmpty = list.isEmpty(); // false4. Iterating through the ArrayList
Being part of the Collection framework, we can use quite a few ways to iterate over the elements of an ArrayList.
4.1. Using ListIterator
The ArrayList‘s listIterator() method returns the iterator of type ListIterator. It allows traversing the list in either direction, modifying the list during iteration, and obtaining the iterator’s current position in the list.
ListIterator<String> listIterator = list.listIterator();
while (listIterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(listIterator.next());
}It is worth mentioning that the remove() and set() methods in ListIterator are not defined in terms of the cursor position; they are defined to operate on the last element returned by a call to next() or previous().
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(List.of("a", "b", "c", "d"));
ListIterator<String> listIterator = list.listIterator();
while (listIterator.hasNext()) {
if(listIterator.next().equalsIgnoreCase("c")){
listIterator.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(list); // [a, b, d]4.2. Using Enhanced for loop (for-each)
We can also use the for-each loop with the ArrayList.
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(List.of("a", "b", "c", "d"));
list.forEach(e -> {
System.out.println(e);
});5. ArrayList and Java Streams
5.1. Iterating over elements
Apart from forEach() loop and ListIterator, we can use the Stream API to iterate over the elements in the ArrayList. Streams allow us to perform more operations on each element as and when they are processed.
arraylist.stream().forEach(e -> {
System.out.println(e);
});5.2. Filtering elements
Stream filtering helps in finding a sublist of elements from the list matching certain criteria. For example, we can find all even numbers from a list of numbers as follows:
ArrayList<Integer> numbersList = new ArrayList<>(List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
numbersList.stream()
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 0)
.forEach(System.out::println); // 2 45.3. Reducing elements with reduce()
The reducing operation is extremely helpful in processing each element in the list using streams and collecting the results in another list. Note that the original stream can come from any data structure/collection type, the toList() method always returns a list of results after processing the stream.
ArrayList<Integer> numbersList = new ArrayList<>(List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
List<Integer> evenNumList = numbersList.stream()
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 0)
.toList();In the above example, the evenNumList is mutable and of type List. If we want to collect the elements in an ArrayList instance specifically, we can use the Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new) to create a new ArrayList and collect elements into it.
ArrayList<Integer> numbersList = new ArrayList<>(List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
ArrayList<Integer> evenNumList = numbersList.stream()
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 0)
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));5.4. Mapping elements with map()
The Stream.map() operation can help in applying a certain logic on each element of the stream in a concise manner. For example, in the stream of numbers, we can square each number and collect into a new list.
List<Integer> squareList = numbersList.stream()
.map(n -> n * n)
.toList();
System.out.println(squareList); // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]6. Sorting an ArrayList
Sorting is an essential task when processing data received from other sources. To sort an ArrayList, we can take advantage of either Collections.sort() for natural sorting order, or implement a custom sorting order by implementing Comparable or Comparator interfaces.
6.1. Natural Ordering with Collections.sort()
The Collections.sort() sorts the specified list into ascending order, according to the natural ordering of its elements. All elements in the list must implement the Comparable interface.
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(List.of(2, 1, 4, 5, 3));
Collections.sort(arrayList);
System.out.println(arrayList); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]For custom objects, we can define the natural order in the custom objects by implementing the Comparable interface.
class Item implements Comparable <Item>{
long id;
String name;
//...
@Override
public int compareTo(Item item) {
if(item.getName() == null || this.getName() == null){
return -1;
}
return item.getName().compareTo(this.getName());
}
}6.2. Custom Ordering Comparator interface
We can apply a custom sorting order using the Comparator instance. We can either use inbuilt Comparators such as Comparator.reverseOrder() or we can create our own implementation.
Collections.sort(arrayList, Comparator.reverseOrder());
System.out.println(arrayList); // [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]To create a custom Comparator, we can create an instance by comparing appropriate fields based on requirements, and pass the comparator to sort() method. The following example compares the names of the items in their natural order.
ArrayList<Integer> itemList = ...;
Comparator<Item> customOrder = Comparator.comparing(Item::getName);
Collections.sort(itemList, customOrder);7. Searching for elements in ArrayList
7.1. Linear search using contains(), indexOf() and lastIndexOf()
The search-related methods in ArrayList perform a linear search by iterating through the elements one by one until the desired element is found or until the end of the list is reached.
Generally, the following 3 methods are used to search an element in the ArrayList:
contains(e): returns true if the list contains at least one specified element, else returns false.indexOf(e): returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in the list, or-1if this list does not contain the element.lastIndexOf(e): returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in the list, or-1if this list does not contain the element.
ArrayList<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<>(List.of(1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 4, 5));
System.out.println( numList.contains(2) ); //true
System.out.println( numList.contains(8) ); //false
System.out.println( numList.indexOf(4) ); //4
System.out.println( numList.lastIndexOf(4) ); //67.2. Binary search using Collections.binarySearch()
In large arraylists, we can take advantage of the binary search algorithm to improve the performance using Collections.binarySearch() method.
Note that the list must be sorted for the binary search to work correctly.
Also, if the list contains multiple elements equal to the specified object, there is no guarantee that one will be found. For example, in numList, element 4 appears 3 times. This method may return the index of any of the 3 elements.
ArrayList<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<>(List.of(1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 4, 5));
Collections.sort(numList);
int foundIndex = Collections.binarySearch(numList, 4); //58. Synchronization and Thread Safety
The ArrayList class is not thread-safe. Using it in a concurrent environment may give inconsistent results. We can use the following techniques to create a thread-safe arraylist.
8.1. Making ArrayList thread-safe with Collections.synchronizedList()
The Collections.synchronizedList() method returns a synchronized (thread-safe) list backed by the specified list. All methods will be synchronized and can be used for add/remove operations in concurrent environments.
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> synchronizedList = Collections.synchronizedList(arrayList);
synchronizedList.add("a"); //thread-safe operationNote that even though all the add/remove/get/set methods are thread-safe, the iterator is still not thread-safe and must be manually synchronized.
List<String> synchronizedList = Collections.synchronizedList(arrayList);
...
synchronized (synchronizedList) {
Iterator i = synchronizedList.iterator(); // Must be in synchronized block
while (i.hasNext()) {
foo(i.next());
}
}8.2. Using CopyOnWriteArrayList for Concurrent Access
The CopyOnWriteArrayList is a thread-safe variant of ArrayList in which all mutative operations (add, set, and so on) are implemented by making a fresh copy of the underlying array.
The CopyOnWriteArrayList is a good alternative when iterations vastly outnumber the mutation operations. It is useful when you cannot or don’t want to synchronize traversals, yet need to preclude interference among concurrent threads.
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> concurrentList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(arrayList);
//all operations are thread-safe
concurrentList.add("a");
for (String token : concurrentList) {
System.out.print(token);
}It is good to know that because CopyOnWriteArrayList creates a new copy of the array in each mutation operation, we won’t encounter the ConcurrentModificationException, even if other threads are modifying the list.
9. SubList of an ArrayList
9.1. Using subList()
The subList(fromIndex, toIndex) method returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive. If fromIndex and toIndex are equal, the returned list is empty.
ArrayList<Integer> origList = new ArrayList<>(List.of(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9));
List<Integer> subList = origList.subList(2, 6); // [2, 3, 4, 5]Note that returned list is backed by the original list, so all add/remove changes in the sublist are reflected in the original list, and vice-versa.
subList.add(10);
System.out.println(origList); // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 6, 7, 8, 9]9.2. Using Streams
The list.stream().filter(…).toList(…) can also be used if we want a sublist of only the elements matching certain criteria. It does not require passing the from and to indices.
ArrayList<Integer> origList = new ArrayList<>(List.of(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9));
List<Integer> subListWithStream = origList.stream()
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 0)
.toList();10. Performance and Time Complexity of ArrayList Operations
The performance of ArrayList operations varies from method to method. The methods which do not require moving other elements or list resizing perform best with O(1), whereas other methods perform O(n) in worst cases when they need to move all the elements in the array.
add(e): takes constant time of O(1) because it always appends at the end of the list. However, in the worst case, if the resizing happens, the time complexity is O(n), where n is the current size of the ArrayList.add(index, e)andremove(e): have a time complexity of O(n), as it may need to shift existing elements.get(i)andset(i, e): have a constant time complexity of O(1) due to the direct index-based access to the element.contains(),indexOf()andlastIndexOf(): have a time complexity of O(n) because they internally use the linear search.
11. FAQs
11.1. Difference between ArrayList and Array
In Java, arrays and arraylist, both, are used to store collections of elements as an ordered collection and provide index-based access to the elements. Still there are few differences as discussed:
- Arrays are fixed size data structures and cannot be changed once created. The arraylist acts as a resizable array that grows/shrinks dynamically when we add/remove elements from it.
- The ArrayList provides the type-safety using Generics. Arrays do not provide such typesafely and may cause ClassCastException in runtime.
- The ArrayListis part of Collections framework and thus provides inbuilt utility methods that transparently store and retrieve the elements from it. When using arrays, we need to manually iterate and keep track of the array indices and element types.
11.2. Difference between ArrayList and LinkedList
Though ArrayList and LinkedList, both seems same in the functionality, yet they differ a lot in how they store and process the elements.
- ArrayList is implemented as a dynamic array, whereas LinkedList is implemented as a doubly-linked list, where each element (node) contains both the data and references to the previous and next elements in the list.
- During add operations, if the list size limit reaches then resizing is performed. In LinkedList, resizing is not needed because new elements are always added as node and only the next and previous references are adjusted.
- ArrayList requires less memory as it stores the element in array and tracks them using array index. The LinkedList requires more memory as it needs to maintain the references to previous and next elements.
- ArrayList is suitable when list iteration outnumbers the mutations. The LinkedList performs better when mutations are more in comparison to iterations.
12. Conclusion
The Java ArrayList class is an excellent utility class to store elements in insertion order and perform various operations on them. Being part of the collection framework makes it even more attractive as it integrates well with other classes and interfaces, and streams.
Happy Learning !!

Comments