JUnit 5 test suites are written with @Suite annotation. Suites help us run the tests spread into multiple classes and packages.
We can use Include and Exclude annotations (discussed later in this tutorial) for filtering test packages, test classes, or even test methods.
@Suite
@SuiteDisplayName("JUnit Platform Suite Demo")
@SelectPackages("com.example.app")
@IncludePackages({"com.example.app.moduleA", "com.example.app.moduleB"})
@IncludeClassNamePatterns("^.*Tests?$")
@ExcludeTags("qa")
public class SuiteDemo {
}
@RunWith(JUnitPlatform.class)has been deprecated in favor of@Suiteannotation and will be removed in JUnit Platform 2.0.
1. Project Structure and Maven Dependency
For this example, we are using the below project structure.
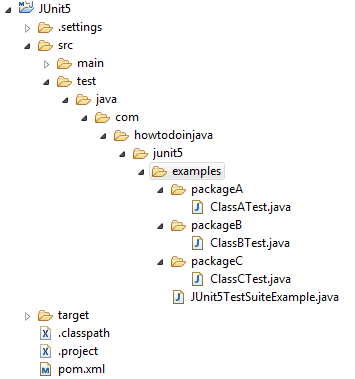
To run the suites, include the latest version of junit-platform-suite dependency (version 1.8 or later).
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-suite</artifactId>
<version>1.11.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>2. Creating Junit 5 Suites
2.1. Using @Suite Annotation
Creating suites is easy. Just add the @Suite annotation of a class and start including or excluding the test classes and methods into the suite.
When we want to run the suite, simply run it as a normal JUnit test class and it will execute all the included tests in the suite.
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.IncludeTags;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.SelectPackages;
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.Suite;
@SelectPackages({"com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples.packageA"
,"com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples.packageB"})
@IncludeTags("production")
@Suite
public class JUnit5TestSuiteExample {
}
3.2. Suite Display Name in Reports
Use @SuiteDisplayName annotation to give a display name for the annotated test class that is executed as a test suite on the JUnit Platform.
Display names are typically used for test reporting in IDEs and build tools and may contain spaces, special characters, and even emojis.
@Suite
@SuiteDisplayName("A demo Test Suite")
@SelectPackages("com.example.app")
public class JUnit5TestSuiteExample {
}3. Including and Excluding Tests in the Suite
JUnit 5 provides two kinds of annotations to include or exclude the tests in the suites i.e. @Select and @Include/@Exclude annotations.
- The @Select annotations specify the packages and classes where JUnit should scan for tests.
- The @Include/@Exclude annotations specify additional conditions to include or exclude previously found tests using the @Select annotation.
We cannot use an independent @Include/@Exclude annotation on a test suite. It must be used with a @Select annotation.
// Valid Use
@Suite
@SelectPackages("example")
@IncludeClassNamePatterns(".*Tests")
class SuiteDemo {
}
// Invalid Use - @Include annotation must be mixed with @Select annotation
@Suite
@IncludeClassNamePatterns(".*Tests")
class SuiteDemo {
}| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
| @SelectClasses | Specifies individual test classes or test methods to include in the test suite. |
| @SelectPackages | Specifies packages (and sub-packages) from which to include test classes for execution. |
| @IncludePackages @ExcludePackages | Filters and includes/excludes sub-packages from the already selected packages using @SelectPackages. |
| @IncludeClassNamePatterns @ExcludeClassNamePatterns | Filters and includes/excludes test classes using specified regex from the already selected packages using @SelectPackages. |
| @IncludeTags @ExcludeTags | Filters and includes/excludes test classes or methods with specific tags from the already selected packages/classes using @SelectPackages and @SelectClasses. |
Let’s learn about these annotations in detail.
3.1. @SelectPackages
@SelectPackages specifies the names of packages to select when running a test suite via @RunWith(JUnitPlatform.class).
3.1.1. Specify Single Package
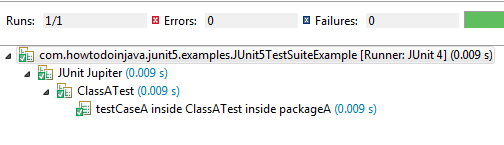
Pass “packageName” as parameter to @SelectPackages annotation.
@Suite
@SelectPackages("com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples.packageA")
public class JUnit5TestSuiteExample
{
}
3.1.2. Specify Multiple Packages
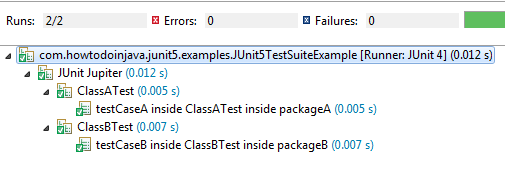
Pass package names in the parameter as a string array (inside curly braces {}) to @SelectPackages annotation.
@Suite
@SelectPackages({"com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples.packageA",
"com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples.packageB"})
public class JUnit5TestSuiteExample
{
}
Please note that if we pass ‘com.demo.app’ in
@SelectPackagesannotation, then test classes present in the package ‘com.demo.app’ AND all it’s sub-packages will be selected for test suite.
3.2. @SelectClasses
@SelectClasses specifies the classes to select when running a test suite via @RunWith(JUnitPlatform.class).
3.2.1. Specify Single Test Class
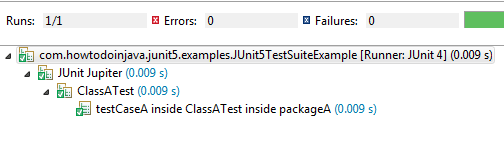
Pass ClassName.class as parameter to @SelectClasses annotation.
@Suite
@SelectClasses( ClassATest.class )
public class JUnit5TestSuiteExample
{
}
3.2.2. Specify Multiple Test Classes
Pass class names in the parameter as array (inside curly braces {}) to @SelectClasses annotation.
@Suite
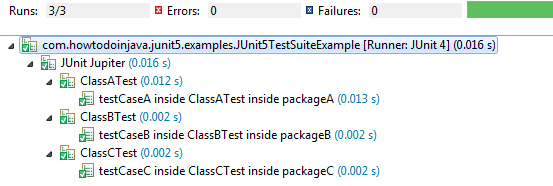
@SelectClasses( { ClassATest.class, ClassBTest.class, ClassCTest.class } )
public class JUnit5TestSuiteExample
{
}
3.3. @IncludePackages and @ExcludePackages
As we learn that @SelectPackages causes all its sub-packages as well to be scanned for test classes.
If you want to exclude any specific package or include any package then you may use @IncludePackages and @ExcludePackages annotations.
3.3.1. @IncludePackages Example
@Suite
@SelectPackages("com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples")
@IncludePackages("com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples.packageC")
public class JUnit5TestSuiteExample
{
}This will add tests from test classes in com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples.packageC only i.e. ClassCTest.
3.3.2. @ExcludePackages Example
@Suite
@SelectPackages("com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples")
@ExcludePackages("com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples.packageC")
public class JUnit5TestSuiteExample
{
}This will add tests from test classes in com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples but exclude all test classes from sub-package com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples.packageC i.e. ClassATest and ClassBTest.
3.4. @IncludeClassNamePatterns and @ExcludeClassNamePatterns
Many times it is not feasible to include all packages or test class names in select annotations. In that case, you may give a broader package scope and apply filtering on which test classes to be included or excluded from the suite.
To specify test class names patterns to exclude or include, you can use @IncludeClassNamePatterns and @ExcludeClassNamePatterns annotations.
3.4.1. @IncludeClassNamePatterns Example
Include all test classes with names ending with ATest or ATests.
@Suite
@SelectPackages("com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples")
@IncludeClassNamePatterns({"^.*ATests?$"})
public class JUnit5TestSuiteExample
{
}3.4.2. @ExcludeClassNamePatterns Example
Exclude all test classes with names ending with ATest or ATests.
@Suite
@SelectPackages("com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples")
@ExcludeClassNamePatterns({"^.*ATests?$"})
public class JUnit5TestSuiteExample
{
}You may apply more than one pattern in above annotations. In case of multiple patterns, they are combined using
ORsemantics.It means that if fully qualified name of a class matches against at least one of the patterns, the class will be included/excluded from the test suite.
3.5. @IncludeTags and @ExcludeTags
In enterprise applications, you may have tagged test cases that you want to run in specific environments e.g. development or production. You can include or exclude tests based on these tags as well, from a test suite.
3.5.1. @IncludeTags Example
This test suite will run all tests tagged with production inside package com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples (and its sub-packages).
@Suite
@SelectPackages("com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples")
@IncludeTags("production")
public class JUnit5TestSuiteExample
{
}3.5.2. @ExcludeTags Example
This test suite will exclude all tests tagged with development inside package com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples (and it’s sub-packages).
@Suite
@SelectPackages("com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples")
@ExcludeTags("development")
public class JUnit5TestSuiteExample
{
}Clearly, there are multiple ways to create test suites in JUnit 5 and it has strong support for filtering tests to/from test suites.
4. Running a Single Test Suite
By default mvn test will run all the tests and suites in the application.
Use Maven surefire plugin’s configuration and test elements to include the test suites and classes in the test execution. In the following example, we are executing a single suite TempDirectoryTestSuite.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0-M7</version>
<configuration>
<test>com.howtodoinjava.junit5.examples.suites.TempDirectoryTestSuite</test>
</configuration>
</plugin>I tried to run the above suite from command line using the JVM system property
test, but it was executing all the tests and suite in the application. Let me know if it works for you.
If we want to exclude few tests classes and suites, we can use the exclude tag.
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>some test to exclude here</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>Happy Learning !!


Comments