Learn to execute JUnit 5 tests in Eclipse IDE. Maven has been used to import dependencies in this JUnit 5 example.
1. Add JUnit 5 Maven Dependencies
To run JUnit 5 tests in Eclipse, at minimum, we will need the latest versions of the following dependencies.
junit-platform-runner(test scope) : provides API and tools used by the IDEs.junit-jupiter-api(test scope) : provides classes and annotations for writing tests, including the@Testannotation. It is transitively included when we include junit-jupiter-engine.junit-jupiter-engine(test scope) : implementation of the Engine API for JUnit Jupiter.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.howtodoinjava</groupId>
<artifactId>JUnit5Examples</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>${maven.compiler.source}</maven.compiler.target>
<junit.jupiter.version>5.8.1</junit.jupiter.version>
<junit.platform.version>1.8.1</junit.platform.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-runner</artifactId>
<version>${junit.platform.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.2</version>
<configuration>
<argLine>
--illegal-access=permit
</argLine>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.2</version>
<configuration>
<argLine>
--illegal-access=permit
</argLine>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>2. Use @Test Annotation on Test Methods
Use the org.junit.jupiter.api.Test class for adding @Test annotation on test methods. Also, add the lifecycle methods as required.
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Disabled;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Tag;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class AppTest {
@BeforeAll
static void setup(){
System.out.println("@BeforeAll executed");
}
@BeforeEach
void setupThis(){
System.out.println("@BeforeEach executed");
}
@Tag("DEV")
@Test
void testCalcOne()
{
System.out.println("======TEST ONE EXECUTED=======");
Assertions.assertEquals( 4 , Calculator.add(2, 2));
}
@Tag("PROD")
@Disabled
@Test
void testCalcTwo()
{
System.out.println("======TEST TWO EXECUTED=======");
Assertions.assertEquals( 6 , Calculator.add(2, 4));
}
@AfterEach
void tearThis(){
System.out.println("@AfterEach executed");
}
@AfterAll
static void tear(){
System.out.println("@AfterAll executed");
}
}
3. Demo
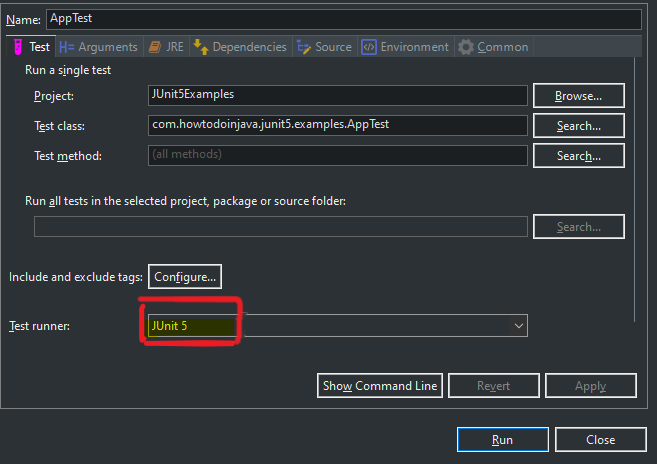
Now run the tests as JUnit 5 test cases in Eclipse.
If it asks you to choose the runtime configuration, select JUnit 5 from the drop down.
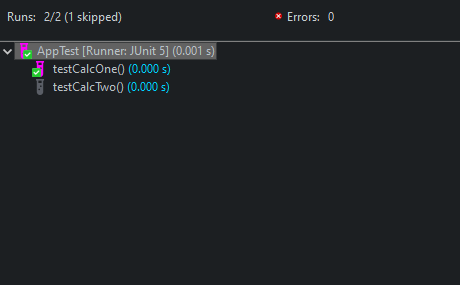
Once we run the tests, notice the output.
Happy Learning !!


Comments