Spring Method Security with Protect-Pointcut is a mechanism to apply security at the method level based on AOP-style expressions (pointcuts). This allows the Spring security configuration to be segregated from the application code.
1. Setup
Start with adding the required Maven dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
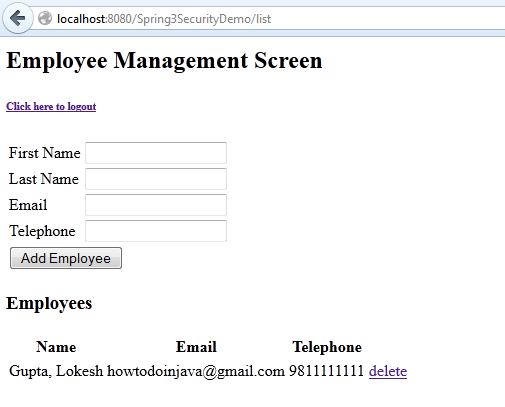
</dependency>In this example, We have used a typical employee management screen. There are two basic operations, ADD and DELETE.
- Add requires an authenticated user to have either “ROLE_USER” or “ROLE_ADMIN“.
- Delete is more protected and requires admin access i.e. only
ROLE_ADMINare allowed to delete a user.
I have two users in the application i.e. admin and lokesh. The admin user has both roles, “ROLE_USER” and “ROLE_ADMIN“, but another user lokesh has only “ROLE_USER” access.
<user-service>
<user name="lokesh" password="password" authorities="ROLE_USER" />
<user name="admin" password="password" authorities="ROLE_USER,ROLE_ADMIN" />
</user-service>Above security configuration will allow both users to add a user, but only admin should be able to delete a user.
Let’s look at major functional points in an example application.
2. Spring Security using Protect-Pointcut
The following configuration enables method-level security using pointcut expressions to specify which methods require specific roles to execute. These rules are applied to methods in the service layer.
<global-method-security>: Enables method security in the application.<protect-pointcut>: Defines security rules using AspectJ-style pointcut expressions.expression: Matches specific methods to secure.execution(* com.howtodoinjava.service.*Impl.add*(..)): Matches any method in classes ending with*Implin thecom.howtodoinjava.servicepackage, whose name starts withadd.execution(* com.howtodoinjava.service.*Impl.delete*(..)): Matches any method in the same package whose name starts withdelete.
access: Specifies the required role to access the matched method.ROLE_USER: Users with theROLE_USERrole can accessadd*methods.ROLE_ADMIN: Users with theROLE_ADMINrole can accessdelete*methods.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-3.0.3.xsd">
<global-method-security>
<protect-pointcut expression="execution(* com.howtodoinjava.service.*Impl.add*(..))" access="ROLE_USER"/>
<protect-pointcut expression="execution(* com.howtodoinjava.service.*Impl.delete*(..))" access="ROLE_ADMIN"/>
</global-method-security>
<http auto-config="false" use-expressions="true">
<intercept-url pattern="/login" access="permitAll" />
<intercept-url pattern="/logout" access="permitAll" />
<intercept-url pattern="/accessdenied" access="permitAll" />
<intercept-url pattern="/**" access="hasRole('ROLE_USER')" />
<form-login login-page="/login" default-target-url="/list" authentication-failure-url="/accessdenied" />
<logout logout-success-url="/logout" />
</http>
<authentication-manager alias="authenticationManager">
<authentication-provider>
<user-service>
<user name="lokesh" password="password" authorities="ROLE_USER" />
<user name="admin" password="password" authorities="ROLE_USER,ROLE_ADMIN" />
</user-service>
</authentication-provider>
</authentication-manager>
<beans:bean id="employeeDAO" class="com.howtodoinjava.dao.EmployeeDaoImpl" />
<beans:bean id="employeeManager" class="com.howtodoinjava.service.EmployeeManagerImpl" />
</beans:beans>3. Manager Class with Secured Methods
package com.howtodoinjava.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.howtodoinjava.dao.EmployeeDAO;
import com.howtodoinjava.entity.EmployeeEntity;
@Service
public class EmployeeManagerImpl implements EmployeeManager {
@Autowired
private EmployeeDAO employeeDAO;
@Override
@Transactional
public void addEmployee(EmployeeEntity employee) {
employeeDAO.addEmployee(employee);
}
@Override
@Transactional
public List<EmployeeEntity> getAllEmployees() {
return employeeDAO.getAllEmployees();
}
@Override
@Transactional
public void deleteEmployee(Integer employeeId) {
employeeDAO.deleteEmployee(employeeId);
}
public void setEmployeeDAO(EmployeeDAO employeeDAO) {
this.employeeDAO = employeeDAO;
}
}I am skipping the rest of the code because it is completely identical to the previous security example using annotations. Also, you can download the source code if anything needs to be referred to.
4. Demo
1) Login with user “lokesh”
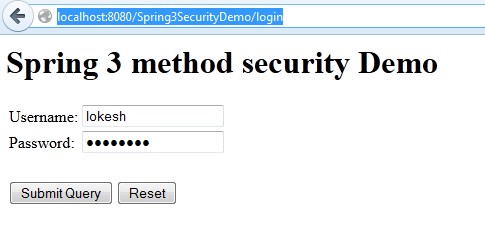
2) Add an employee into the list
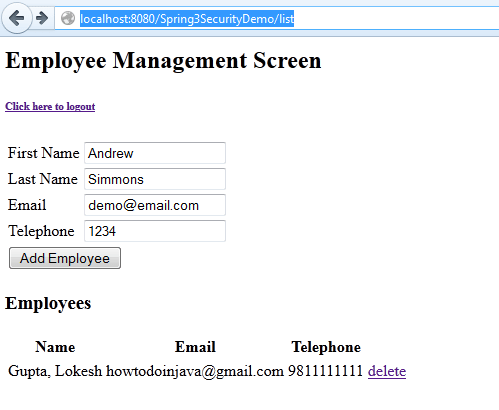
3) User is added successfully
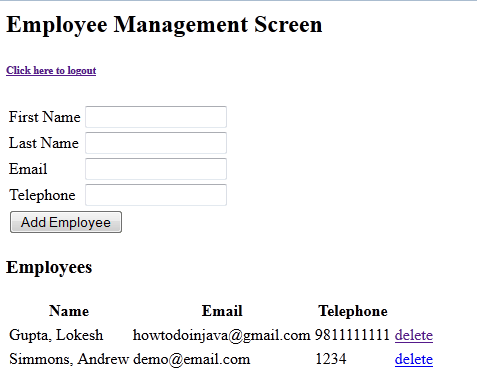
4) Try to delete employee. Access denied.
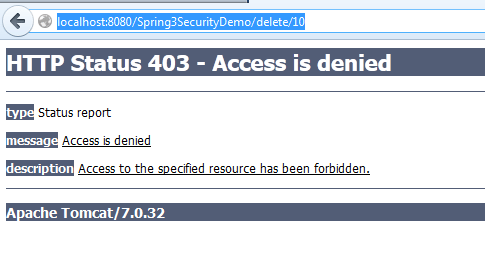
5) Login with admin user
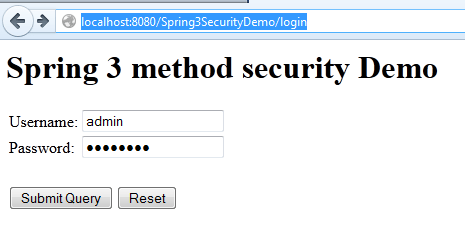
6) Add an employee into the list
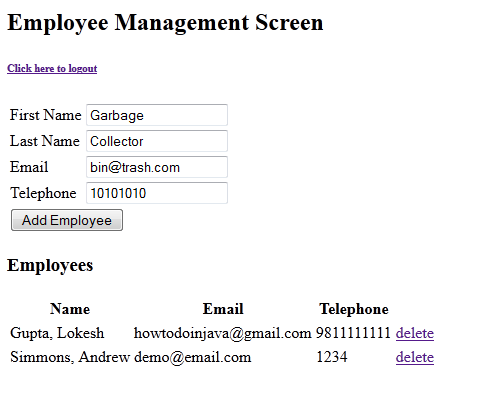
7) User is added successfully
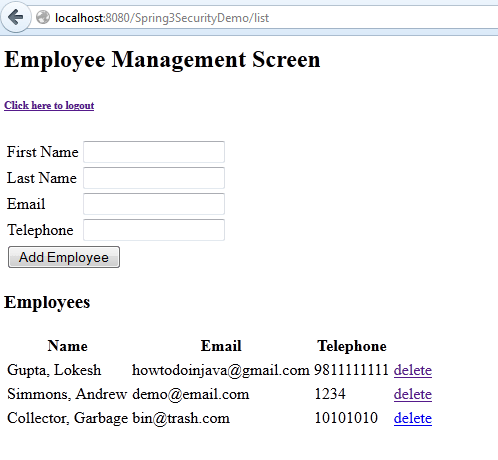
8) Try to delete employee. Employee Deleted.
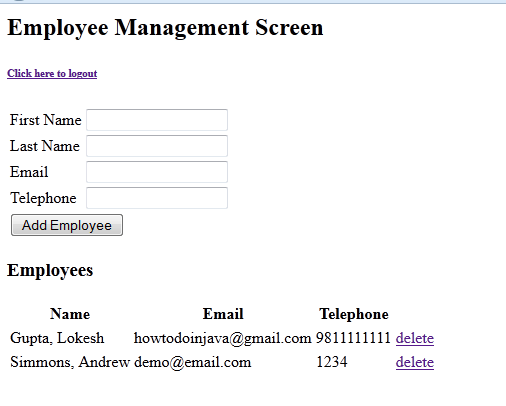
9) Try to delete another employee. Employee Deleted.
Happy Learning !!


Comments