The Spring @Repository annotation is a specialization of the @Component annotation which indicates that an annotated class is a “Repository”, which can be used as a mechanism for encapsulating storage, retrieval, and search behavior which emulates a collection of objects
1. @Repository Annotation
In the spring framework, @Component annotation marks a Java class as a bean so the component-scanning mechanism can find it and create its instance into the application context.
As @Repository serves as a specialization of @Component, it also enables annotated classes to be discovered and registered with the application context.
This annotation is a general-purpose stereotype annotation that can be applied over DAO classes as well as DDD-style repositories. Individual teams may use it as appropriate.
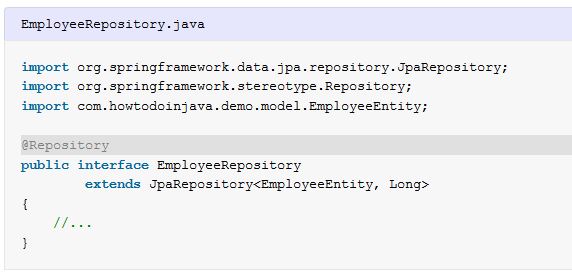
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.howtodoinjava.demo.model.EmployeeEntity;
@Repository
public interface EmployeeRepository
extends JpaRepository<EmployeeEntity, Long>
{
}2. DataAccessException Translation
The @Repository annotation can have a special role when it comes to converting database exceptions to Spring-based unchecked exceptions.
For example, when we work with Hibernate and we do not use a Spring template (e.g. JdbcTemplate) to interact with the database. In this case, if hibernate threw an exception then spring will not convert it to Spring-based exception.
To automatically convert such non-spring exceptions to spring exceptions, we shall annotate Hibernate DAOs with @Repository. This way, PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor will apply persistence exception translation and converts native resource exceptions to Spring’s DataAccessException hierarchy.
3. Testing a @Repository class with @DataJpaTest
Test a repository class is usually done by using an in-memory database and test cases that bootstrap a Spring ApplicationContext usually through the test context framework.
In Spring boot applications, we can use @DataJpaTest annotation that focuses only on JPA components. @DataJpaTest annotation will disable full auto-configuration and instead apply only configuration relevant to JPA tests.
By default, tests annotated with @DataJpaTest are transactional and roll back at the end of each test. They also use an embedded in-memory database.
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.DataJpaTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import com.howtodoinjava.demo.model.EmployeeEntity;
import com.howtodoinjava.demo.repository.EmployeeRepository;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@DataJpaTest
public class EmployeeRepositoryTest
{
@Autowired
EmployeeRepository repository;
@Test
public void testRepository()
{
EmployeeEntity emp = new EmployeeEntity();
emp.setFirstName("Lokesh");
emp.setLastName("Gupta");
emp.setEmail("howtodoinjava@gmail.com");
repository.save(emp);
Assert.assertNotNull(emp.getId());
}
}Drop me your questions related to Spring Boot @Repository example as discussed above.
Happy Learning !!

Comments