Learn to create asynchronous methods in the Spring framework with the help of @Async and @EnableAsync annotations that use a thread pool on top of Java ExecutorService framework.
1. Setting Up @EnableAsync and @Async
Spring comes with @EnableAsync annotation and can be applied to a @Configuration class for asynchronous behavior. The @EnableAsync annotation will look for methods marked with @Async annotation and run them in background thread pools.
The @Async annotated methods are executed in a separate thread and return CompletableFuture to hold the result of an asynchronous computation.
To enable async configuration in spring, follow these steps:
- Create a thread pool to run the tasks asynchronously.
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncConfiguration {
@Bean(name = "asyncExecutor")
public Executor asyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(3);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(3);
executor.setQueueCapacity(100);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("AsynchThread-");
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}- Annotate the method with @Async that shall run asynchronously. The method must be public and may or may not return a value. The return value should be wrapped in a Future interface implementation if it returns a value.
@Async("asyncExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> methodOne() throws InterruptedException {
//code
}
@Async("asyncExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> methodTwo() throws InterruptedException {
//code
}
@Async("asyncExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> methodThree() throws InterruptedException {
//code
}- To combine the result of multiple async tasks, use join() method.
CompletableFuture.allOf(methodOne, methodTwo, methodThree).join();2. Spring REST Controller Example with Async Tasks
In this demo, we will create a REST API that fetches data from three remote services asynchronously. When responses from all three services are available, we will aggregate the responses.
- Invoke EmployeeName API
- Invoke EmployeeAddress API
- Invoke EmployeePhone API
- Wait for responses from the above services
- Aggregate all three API responses and build the final response to send back to the client
2.1. Remote REST APIs to be Consumed Asynchronously
The following are remote APIs that the async REST controller must consume before aggregating the data and returning the result. The following class is only for demo purposes. The actual API may have different methods.
@RestController
public class EmployeeDataController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/address", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getAddress() {
//...
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/phone", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getPhoneNumber() {
//...
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/name", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getEmployeeName() {
//...
}
}2.3. @Async Methods Returning CompletableFuture
These service methods will pull the data from the remote APIs or a database and must run in parallel in separate threads to speed up the process.
@Service
class AsyncService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AsyncService.class);
@Async("asyncExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> getEmployeeName() throws InterruptedException {
log.info("Fetching Employee Name using RestClient/WebClient API...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture("John Doe");
}
@Async("asyncExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> getEmployeeAddress() throws InterruptedException {
log.info("Fetching Employee Address using RestClient/WebClient API...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture("123 Main St, Cityville");
}
@Async("asyncExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> getEmployeePhone() throws InterruptedException {
log.info("Fetching Employee Phone using RestClient/WebClient API...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture("+123456789");
}
}2.3. Invoking Async Methods and Aggregating Results
This is the main API that calls the async methods, consumes and aggregates their responses, and returns to the client.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
class AsyncController {
private final AsyncService asyncService;
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AsyncController.class);
public AsyncController(AsyncService asyncService) {
this.asyncService = asyncService;
}
@GetMapping("/testAsync")
public String testAsync() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
log.info("Starting Async Calls");
CompletableFuture<String> nameFuture = asyncService.getEmployeeName();
CompletableFuture<String> addressFuture = asyncService.getEmployeeAddress();
CompletableFuture<String> phoneFuture = asyncService.getEmployeePhone();
CompletableFuture.allOf(nameFuture, addressFuture, phoneFuture).join();
return "Name: " + nameFuture.get() + ", Address: " + addressFuture.get() + ", Phone: "
+ phoneFuture.get();
}
}3. Exception Handling
When a method return type is a Future, the Future.get() method will throw the exception and we should use try-catch block to catch and handle the exception before aggregating the results.
The problem is if the async method does not return any value then it is hard to know if an exception occurred while the method was executing. We can use AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler implementation for catching and handling such exceptions.
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncConfig extends AsyncConfigurerSupport {
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return new AsyncExceptionHandler();
}
}public class AsyncExceptionHandler implements AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AsyncExceptionHandler.class);
@Override
public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable ex, Method method, Object... params) {
logger.error("Unexpected asynchronous exception at : "
+ method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName(), ex);
}
}4. Run the Demo
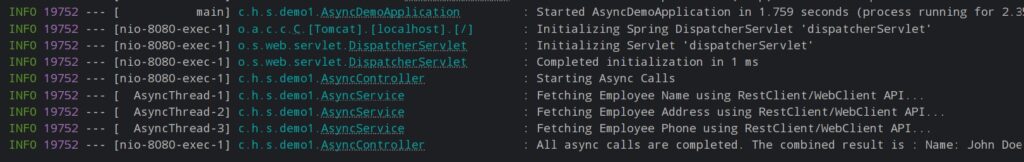
Download and start both applications. Hit the API: http://localhost:8080/api/testAsync. Observe the output in the console.
See how all 3 methods are asynchronously called in separate threads when we use @Async annotation.
With @Async
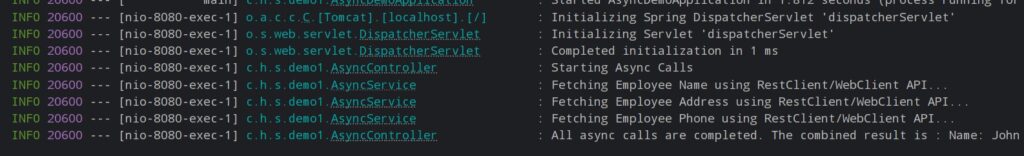
Without @Async
Drop me your questions related to creating a spring boot non-blocking rest API.
Happy Learning !!


Comments