Learn to write spring boot async rest controller using ResponseBodyEmitter. We can use this approach when we have a service, or multiple calls, and want to collect the results and send the response to the client.
ResponseBodyEmitter helps to collect and send the response to the client. ResponseBodyEmitter is returned from a controller method that does the asynchronous request processing and one or more objects are written to the response.
While
DeferredResultis used to produce a single result, aResponseBodyEmittercan be used to send multiple objects where each object is written with a compatibleHttpMessageConverter.
1. How to use ResponseBodyEmitter?
To use ResponseBodyEmitter, create a controller method and create an instance of ResponseBodyEmitter and return it from the method. The instance is handed over to a new thread for request processing. Inside the thread, we use the send() method to send the data/events in a stream.
@RequestMapping(value="/resource-uri", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseBodyEmitter handle()
{
ResponseBodyEmitter emitter = new ResponseBodyEmitter();
// Pass the emitter to a thread for request processing ...
return emitter;
}
// in the new thread
emitter.send(foo1);
// and again
emitter.send(foo2);
// and done
emitter.complete();2. Async REST Controller using ResponseBodyEmitter
In the given controller method, we are accessing the data sets (use your own domain datatypes).
- There is a data service that returns data sets from DB or any other source.
- Each data set is then processed (e.g. retrieving related information from another source) which takes time. This is simulated using an artificial delay by calling
thread.sleep()method. - Each data set is then added to ResponseBodyEmitter object using
emitter.send()method. - Finally
emitter.complete()is called to mark that request processing is complete so that the thread responsible for sending the response can complete the request and be freed up for the next response to handle. - If any error is encountered while request processing, complete the process by
emitter.completeWithError(). The exception will pass through the normal exception handling of Spring MVC and after that, the response is completed.
@RestController
public class DataSetController {
private final DataSetService dataSetService;
public DataSetController(DataSetService dataSetService) {
this.dataSetService = dataSetService;
}
@GetMapping("/fetch-data-sets")
public ResponseBodyEmitter emitDataSets() {
ResponseBodyEmitter emitter = new ResponseBodyEmitter();
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//Creating a new thread for async processing
executor.execute(() -> {
List<DataSet> dataSets = dataSetService.findAll();
try {
for (DataSet dataSet : dataSets) {
randomDelay();
emitter.send(dataSet);
}
emitter.complete();
} catch (IOException e) {
emitter.completeWithError(e);
}
});
executor.shutdown();
return emitter;
}
private void randomDelay() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
3. Async Configuration
To override the default async behavior such as thread pool and timeout, we can implement the WebMvcConfigurer interface and override its configureAsyncSupport() method.
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.AsyncSupportConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureAsyncSupport(AsyncSupportConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.setTaskExecutor(mvcTaskExecutor());
configurer.setDefaultTimeout(30_000);
}
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor mvcTaskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(10);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix("mvc-task-");
return threadPoolTaskExecutor;
}
}4. Test
4.1. Mock Testing with JUnit
To test the above controller method, I am using mockito shipped with spring boot test module.
@WebMvcTest(DataSetController.class)
public class DataSetControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@MockBean
private DataSetService dataSetService;
@Test
public void testFetchData() throws Exception {
Mockito.when(dataSetService.findAll())
.thenReturn(Arrays.asList(new DataSet(BigInteger.valueOf(1), "data")));
MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(get("/fetch-data-sets"))
.andExpect(request().asyncStarted())
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.log())
.andReturn();
mockMvc.perform(asyncDispatch(mvcResult))
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.log())
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().json("{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"data\"}"));
}
}Program output.
MockHttpServletResponse:
Status = 200
Error message = null
Headers = {}
Content type = null
Body = {"id":1,"name":"data"}
Forwarded URL = null
Redirected URL = null
Cookies = []4.2. Browser testing
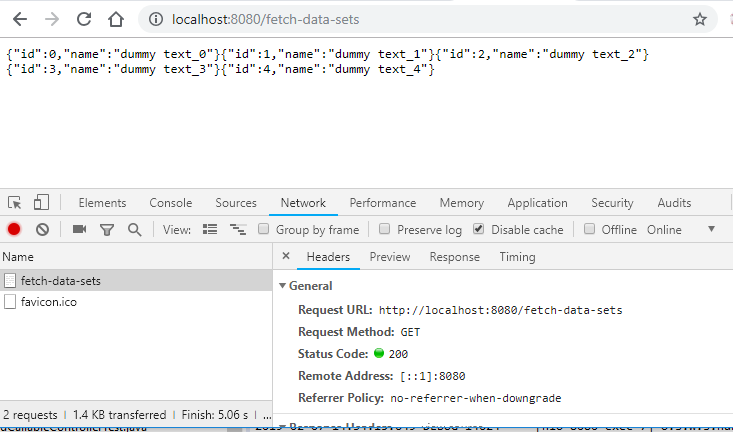
To test in browser, start the application using class SpringAsyncExampleApplication and hit the URL in browser: http://localhost:8080/fetch-data-sets
Check the response returned from server after some delay.
Let me know if you face any errors while executing this Spring Boot async rest controller example using ResponseBodyEmitter.
Happy Learning !!

Comments